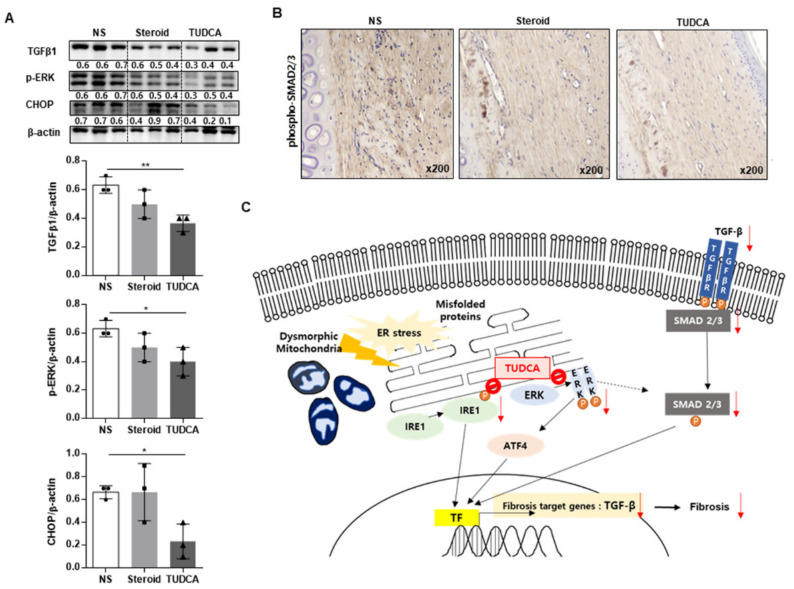
Figure 6.
Effects of TUDCA on scar formation compared to saline or steroid, through the reduction of ER stress signaling TGF-β. (A) Western blot analysis of TGF-β1, phospho-ERK, CHOP, and β-actin expression in rabbit ear scars in the normal saline (NS), steroid, and TUDCA groups (n = 3 for each group). Densitometry of Western blot analysis in rabbit ear scars from the NS, steroid, and TUDCA groups (n = 3 biological replicates). (B) Representative images of phospho-SMAD2/3 expression in rabbit ear scars in the normal saline, steroid, and TUDCA groups using IHC (n = 5 for each group). (C) Proposed mechanism of TUDCA treatment in keloid formation. Transcription factor (TF) for TGF-β is activated through the AFT4, IRE1, and PERK pathways in keloid tissue. TUDCA inhibits the activation of IRE, ERK, and ATF4, thereby reducing TGF-β TF in the nucleus. Finally, the expression of TGF-β and fibrosis is reduced. Significance was set at p < 0.05. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.