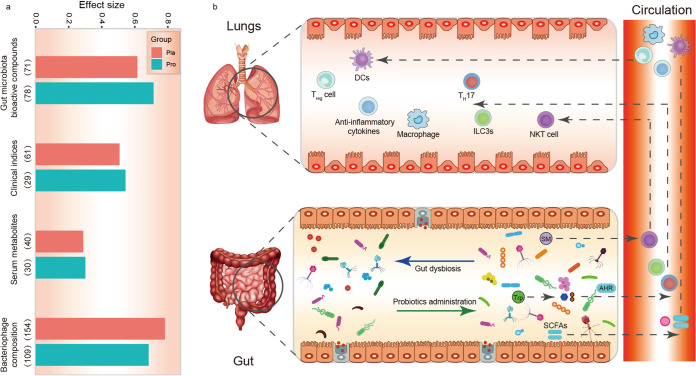
FIG 6.
Effect size of gut microbiota on the variation in the monitored features and proposed model of probiotic-driven pathways modulating the gut-lung axis in asthmatic patients. (a) The effect size of gut microbiota on the monitored features in the probiotic (Pro) and placebo (Pla) groups, including predicted gut bioactive compounds, clinical indexes, serum metabolomes, and virome. The number in parentheses represents the number of gut species-level genome bins (SGBs) that have an impact on the variation in the monitored features. (b) Schematic diagram illustrating key probiotic-driven pathways that modulated the gut-lung axis and host response. DCs, Treg cell, TH17, ILC3s, and NKT cell represent dendritic cells, regulatory T cell, T helper 17, group 3 innate lymphoid cells, and natural killer T cells, respectively. SM, Trp, AHR, and SCFAs represent sphingomyelin, tryptophan, airway hyperresponsiveness, and short-chain fatty acids, respectively.