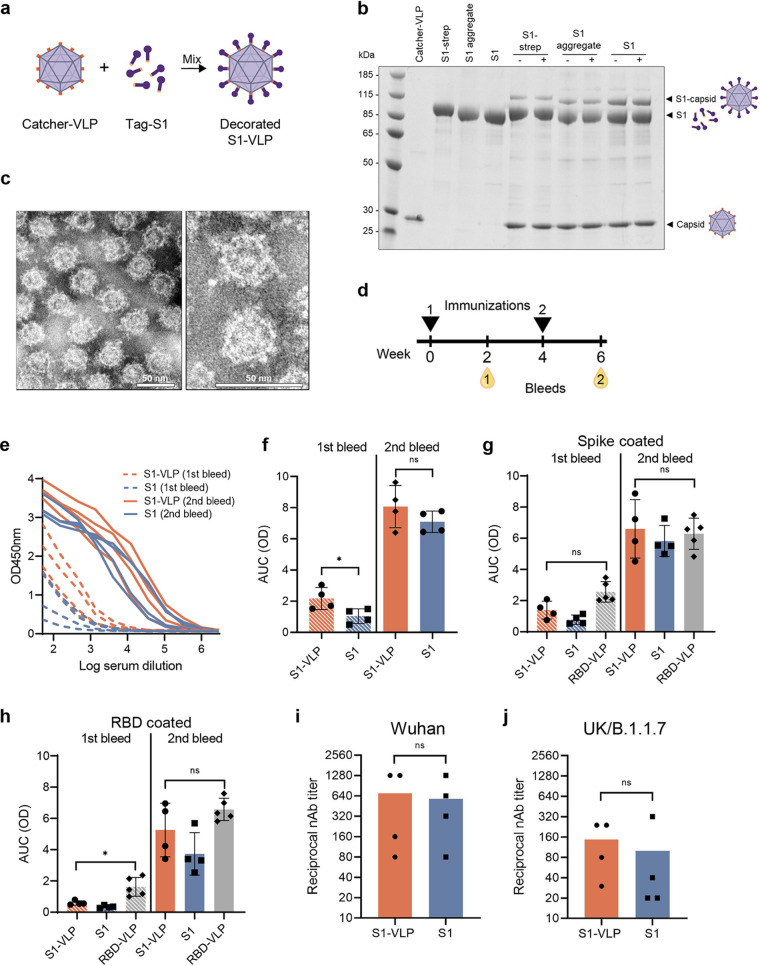
FIG 5.
Low-dose vaccination of BALB/c mice with soluble S1 and S1-VLP induces potent neutralizing antibody responses. (a) S1 was coupled to VLPs by a coupling reaction as schematically represented. The catcher-VLPs are mixed with tag-S1, which results in a covalent display (decorated S1-VLP) that is visible on a reduced, denaturing SDS-PAGE gel. The individual components (catcher-VLP and S1) are shown. (b) Antigens were mixed with VLP and were analyzed again before (−) and after (+) a centrifugation step. An extra band appears representing the covalently fused S1 to a single AP205 capsid (S1-capsid). (c) The VLPs were purified from the uncoupled S1 subunits and visualized by negative-stain transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The scale bar represents 50 nm. (d) BALB/c mice (n = 4 per group) were vaccinated with 0.5 μg soluble S1 or 0.5 μg S1-VLP with Addavax adjuvant. Blood was collected 2 weeks postprime (1st bleed) and 2 weeks postboost (2nd bleed). (e) IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike were analyzed in a dilution series in an ELISA. (f to h) The IgG titers were expressed as area under the curve (AUC) values. (f) The IgG titers in plates coated with SARS-CoV-2 spike were compared for mice vaccinated with S1 or S1-VLP. (h and g) Sera were measured on ELISA plates coated with RBD (g) or coated with full spike (h) and were compared to sera of mice vaccinated twice with 5 μg RBD-VLP. (i and j) The reciprocal neutralizing antibody titers after the second vaccination are shown for neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan (L008) (i) or UK/B.1.1.7 (j) strain. A two-sided nonparametric Mann-Whitney t test was used for statistical comparison. ns, nonsignificant; *, P < 0.05. Significance is marked with an asterisk in panels e (P = 0.0286) and g (P = 0.0159).