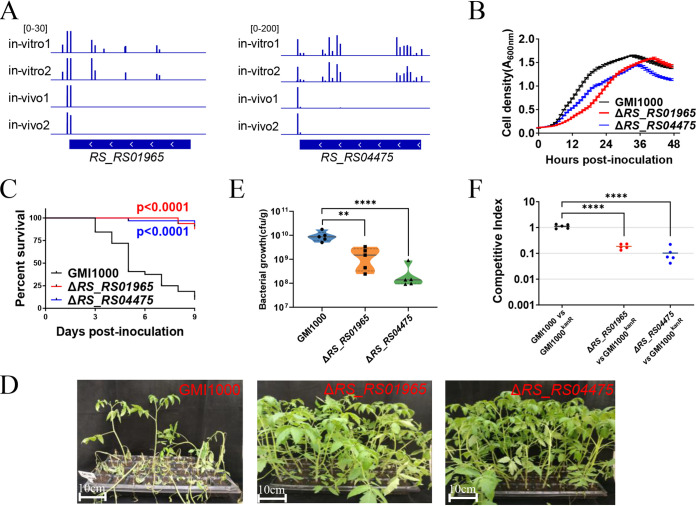
FIG 2.
RS_RS01965 and RS_RS04475 are required for survival in tomato plants. (A) Transposon insertion distribution within RS_RS01965 and RS_RS04475 of transposon insertion libraries in vivo and in vitro. (B) Growth of the ΔRS_RS01965 mutant, the ΔRS_RS04475 mutant, and wild-type strain GMI1000 in BG medium. (C) Survival curve of tomato plants inoculated with the ΔRS_RS01965 mutant, the ΔRS_RS04475 mutant, and wild-type strain GMI1000. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis with the Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon method was used to compare the pathogenicity between the mutant and wild-type strains. A P value of <0.05 was considered significant. (D) Bacterial wilt symptoms of tomato plants 9 days after inoculation with the ΔRS_RS01965 mutant, the ΔRS_RS04475 mutant, and wild-type strain GMI1000. (E) Colonization of ΔRS_RS01965 and ΔRS_RS04475 mutants. The CFU of R. solanacearum strains in 1 g tomato plant stem were counted 5 days postinoculation. Asterisks indicate significant differences (**, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; t test). F. In vivo competitive index of ΔRS_RS01965 and ΔRS_RS04475 mutants. R. solanacearum mutants and GMI1000Kanr were coinoculated into the stems of tomato plants. The competitive index was measured 5 days postinoculation. Asterisks indicate significant differences (****, P < 0.0001; t test).