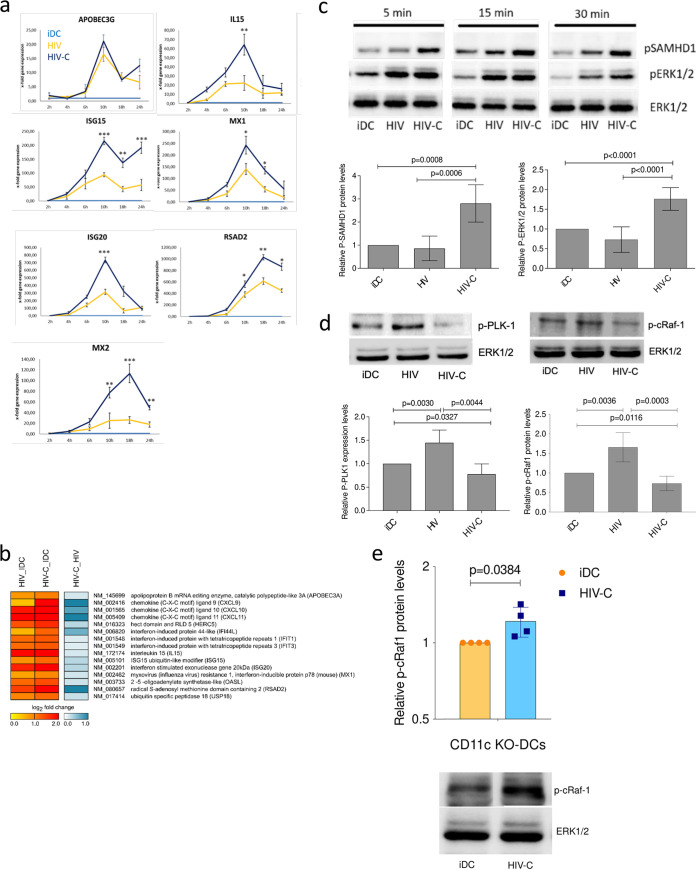
FIG 1.
HIV-C initiates an efficient type I IFN response after HIV-1 infection in DCs. (a) Real-time RT-PCR analyses of APOBEC3G, IL-15, MX1, ISG15, ISG20, MX2, and RSAD2 mRNAs in moDCs after infection as indicated with various differentially opsonized (HIV and HIV-C) HIV-1 strains. RT-PCR was performed in duplicate for each sample, and data are means and standard deviations (SD) for cells from three donors exposed to HIV-1 BaL. Unpaired Student's t test was performed to analyze statistical significance between HIV and HIV-C. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (b) Microarray analyses of HIV- and HIV-C-exposed DCs after 6 h infection with different strains (BaL, 92BR030, and 92UG037). Cells from four donors exposed to either BaL and 93BR030 or BaL and 92UG037 were analyzed. (c) (Top) Representative immunoblot (IB) analyses of phosphorylated SAMHD1 and ERK1/2 and nonphosphorylated ERK1/2 as a loading control of DCs exposed for short times (5, 15, and 30 min) to differentially opsonized HIV-1 BaL (HIV and HIV-C). IB analyses were repeated in five independent experiments. (Bottom) Quantification of SAMHD1 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation at 4 h after HIV exposure using ImageJ for samples from five donors. (d) (Top) Representative IB analyses of phosphorylated PLK1 and c-Raf-1 (Ser338), and nonphosphorylated ERK1/2 as a loading control of DCs exposed for 4 h to differentially opsonized HIV-1 BaL (HIV and HIV-C). (Bottom) Quantification of PLK-1 and c-Raf-1 phosphorylation at 4 h after HIV exposure using ImageJ for samples from three donors. (e) c-Raf-1 phosphorylation was also analyzed in untreated and HIV-C-exposed CD11c-KO DCs. (Top) Relative c-Raf-1 phosphorylation levels in CD11c-KO DCs from four independent experiments; (bottom) representative IB of p-c-Raf-1 and ERK1/2 as a loading control. Unpaired Student's t test was performed to analyze statistical significance between controls or HIV and HIV-C in all analyses.