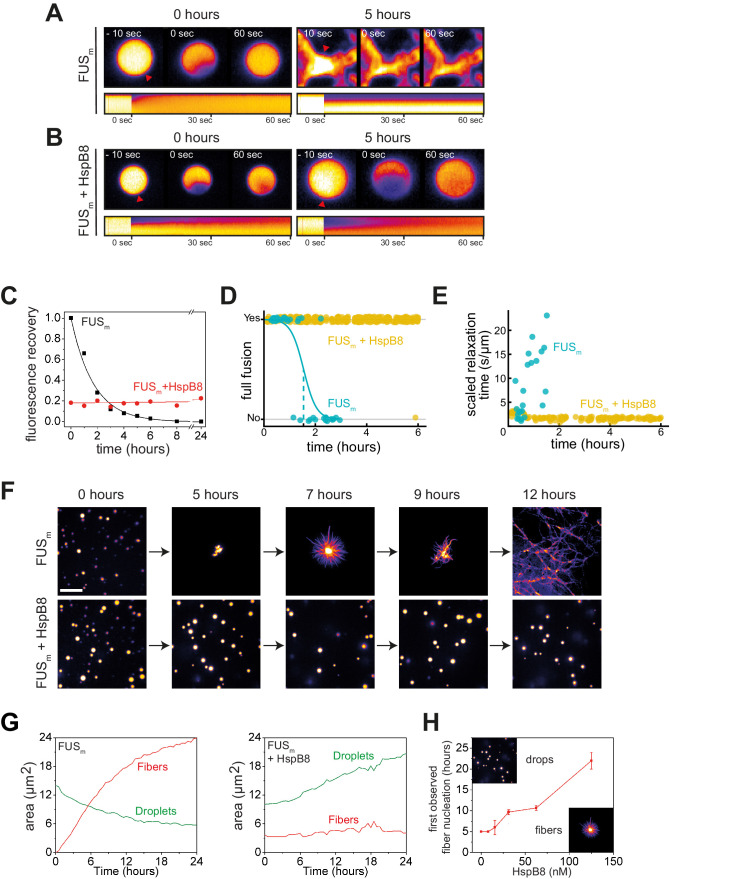
Figure 3. HspB8 prevents hardening and fiber formation of FUS droplets and keeps them dynamic.
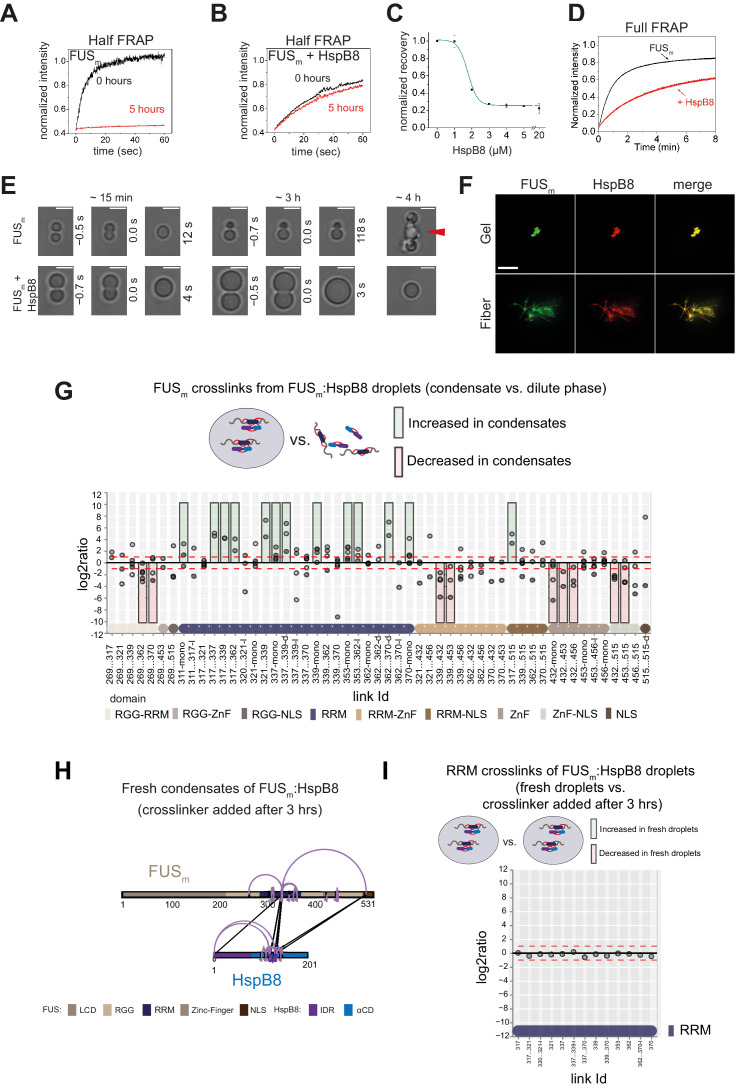
(A) FRAP experiment of fresh FUSm condensates (0 hr) and condensates incubated for 5 hr. A kymograph shown below illustrates the kinetics of the process. (B) FRAP experiment of fresh FUSm condensates mixed with HspB8 (0 hr) and condensates incubated for 5 hr. A kymograph shown below illustrates the kinetics of the process. (C) Kinetics of the FUSm aging process. Plotted are the initial slopes of the FRAP recovery curves for FUSm condensates in the absence (black) or presence of HspB8 (red). (D) Successful complete fusion events were registered over time, demonstrating the aging process of the FUSm sample in the absence (turquoise, N=40) or the presence of HspB8 (yellow, N=330). The half-life of liquid-like FUSm condensates alone was estimated to be around 1.5 hr from logistic regression. (E) The size-normalized coalescence relaxation time is an indicator for the material state of the condensates. While it increases for FUSm condensates during the hardening process, it stays constant over 6 hr in the presence of HspB8. Tweezer experiments were performed with fresh samples of 5 μM FUSm with or without 20 μM HspB8. (F) Aging process of 5 µM FUSm condensates in the absence and presence of 5 µM HspB8. In the presence of the chaperone, the droplet morphology is maintained over the whole timeframe of the experiment (12 hr). Scale bar is 10 µm. (G) Left panel: shown is the total area of droplet material (green line) or fibrous material (red line) within FUSm droplets as a function of time after FUSm droplets were added to the existing fibrous material. Spacing between data points is 30 min. Right panel: shown is the total area of droplet material (green line) and fibrous material (red line) within FUSm droplets as a function of time after FUSm droplets and HspB8 were added to the existing fibrous material. Spacing between data points is 30 min. (H) The onset of 5 µM FUSm fiber formation as a function of HspB8 concentration. FRAP, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching.