Fig 2.
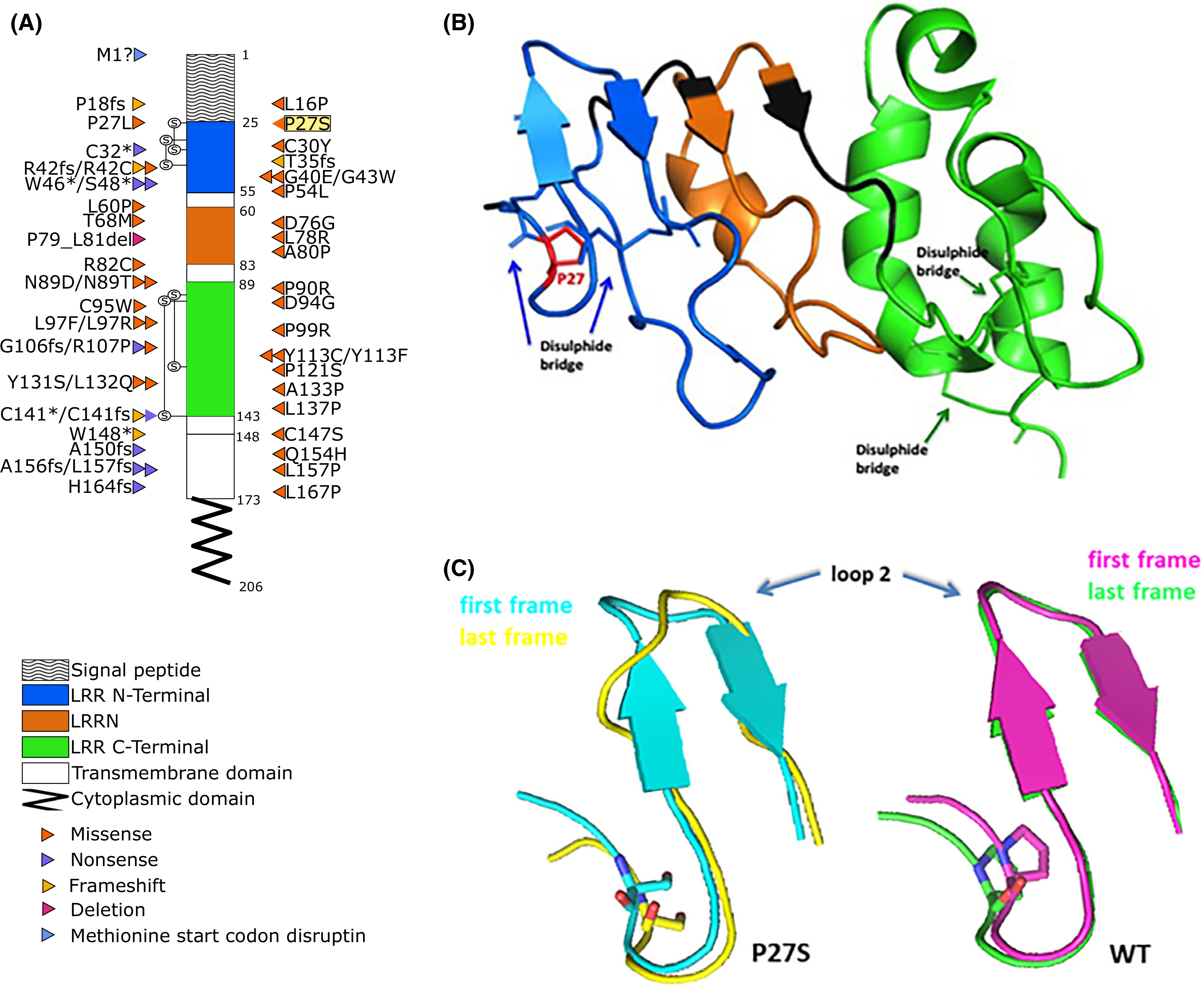
GPIbβ amino acid sequence with BSS-causing mutations and molecular modelling analyses. (A) Positions of the mutations within the coding regions of platelet glycoprotein (GP)Ibβ according to National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Reference Sequence, NP_000398.1. The different domains are indicated with different patterns. Different types of mutation are colour-coded; highlighted in yellow is the Proline27 to Serine27 substitution (P27S) described here first. Known mutations were obtained from: Savoia et al., 201416; Sivapalaratnam et al., 201717; Bragadottir et al., 201510; Qiao et al., 201518; Kunishima et al., 200119; Ferrari et al., 201820; and Bastida et al., 201813. (B) Three-dimensional structure of GPIbβ sequence, colour-coded according to the schematic representation in (A). (C) X-ray structure of protein (26–143 aa code 3RFE) showing the impact of p.P27S on GPIbβ glycoprotein conformation; in particular, the superposition between the first (teal) and last (yellow) frame of the molecular dynamics for the p.P27S protein (left), and the superposition between the first (pink) and last (green) frame for the wild-type (WT) protein (right) are reported.
