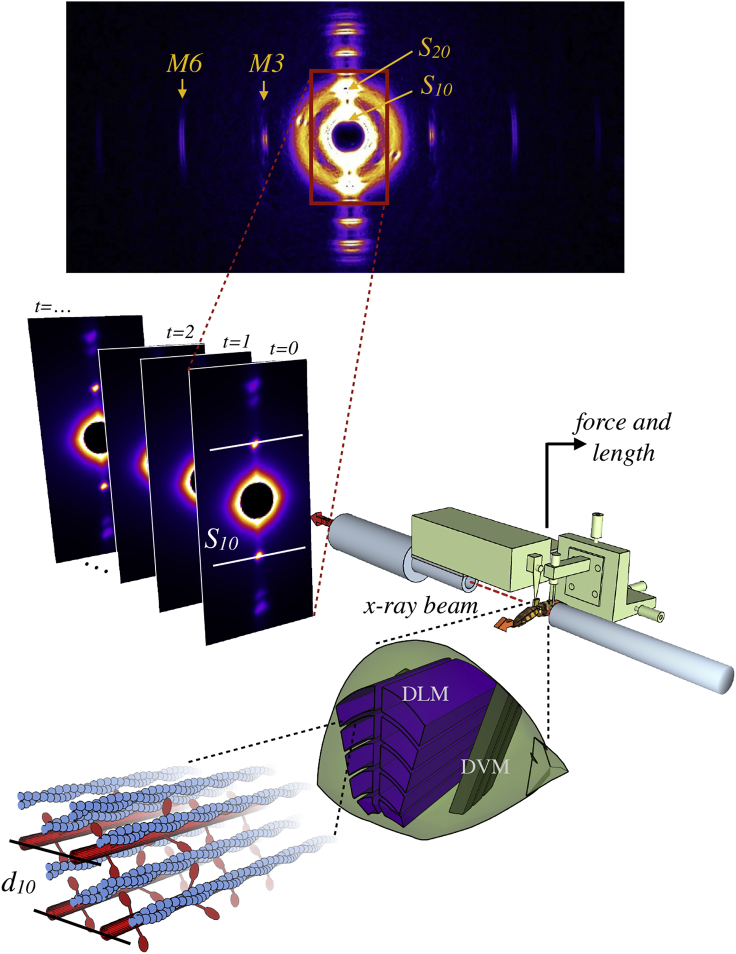
Figure 2.
Schematic of x-ray fiber diffraction procedure for measuring lattice spacing. From bottom left: the lattice of contractile proteins, containing myosin (red) and actin (blue) filaments is shown, with the lattice spacing (d10) marked. Zooming out, these parallel filaments are part of the dorsolongitudinal muscle (DLM, purple), which runs perpendicularly to the dorsoventral muscle (DVM, dark green) in the hawkmoth thorax (light green). The dorsoventral muscles and a strip of exoskeleton are removed, and the mechanically isolated DLM muscles are placed in the synchrotron x-ray diffraction beam (dotted red line). Muscle length is controlled, and the force is measured by a force-feedback motor (light green). As the beam line passes through the sample, the resulting diffraction pattern is recorded on a detector. This is repeated over the course of many contractions, resulting in a series of frames of the x-ray diffraction pattern. On each pattern, two bright spots (marked S10) are used to calculate the d10 interfilament lattice spacing. To see this figure in color, go online.