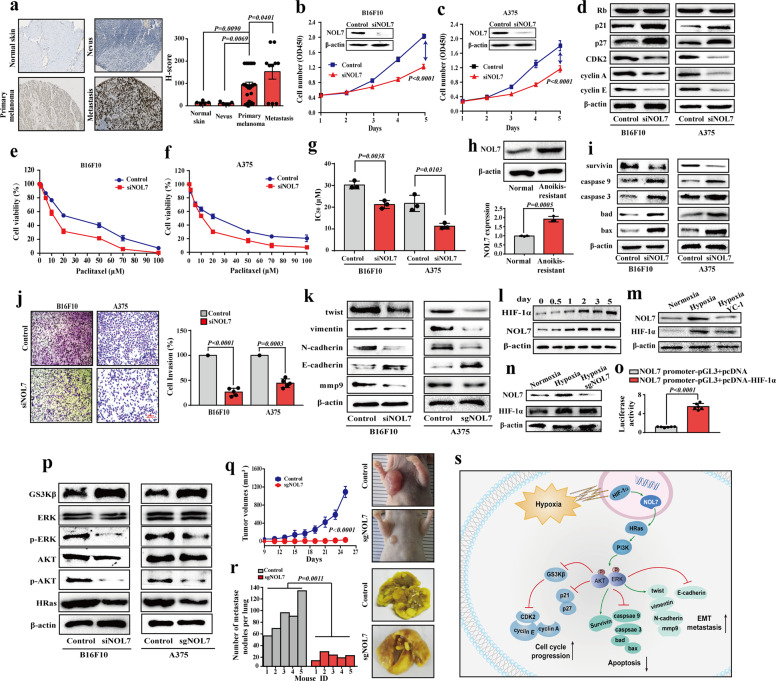
Fig. 1.
NOL7 facilitates melanoma progression and metastasis. a NOL7 expression increases in the disease progression from normal skin and nevus to primary melanoma and further to metastatic melanoma as detected by IHC (left panels). The H-score for the quantification of NOL7 expression is shown on the right panel. b, c Lower cell proliferation upon NOL7 knockdown in B16F10 (b) and A375 (c) cells. Insets illustrate strongly decreased NOL7 levels upon siRNA targeting of NOL7. d Effect of NOL7 knockdown on cell cycle-associated proteins in B16F10 and A375 cells. NOL7 knockdown decreased the expression level of cyclin A, cyclin E, CDK2, and enhanced the expression level of p21 and p27. See Supplementary Fig. S2g, h for quantification. e–g NOL7 knockdown increased sensitivity of B16F10 (e) and A375 (f) cells to paclitaxel. Target cells were incubated with paclitaxel at various concentrations for 24 h and cell viability was tested by the MTT assay. Quantification of IC50 values is shown in (g). h Western blotting shows the upregulation of NOL7 expression in anoikis-resistant A375 cells as compared to normal A375 cells. Quantitative analysis of NOL7 expression is shown below. i Effect of NOL7 knockdown on apoptosis-related proteins in B16F10 and A375 cells. NOL7 knockdown decreased the expression level of survivin and increased the expression level of caspase 3, caspase 9, bad, and bax. See Supplementary Fig. S5b, c for quantification. j Phase micrographs showing the invading B16F10 and A375 cells (control and after NOL7 knockdown) at different time intervals. Quantitative analysis of the effect of NOL7 knockdown on cell invasion of B16F10 and A375 cells is shown on the right. k Effect of NOL7 knockdown on EMT-associated proteins in B16F10 and A375 cells. NOL7 depletion increased the expression level of epithelial marker E-cadherin and decreased the expression level of mesenchymal markers, N-cadherin, mmp9, vimentin, and twist in B16F10 and A375 cells. See Supplementary Fig. S6c, d for quantification. l–n Western blotting shows the concurrent NOL7 and HIF-1α expression under hypoxia (l) plus YC-1 (HIF-1α inhibitor) (m) or upon NOL7 depletion (n). See Supplementary Fig. 9b, c for quantification. o HIF-1α induces NOL7 expression through promoting the NOL7 transcription, as measured in a dual-luciferase reporter assay following transient transfection with the NOL7 promoter-pGL3 plasmid and pcDNA-HIF-1α (or the empty pcDNA). The pRL-TK vector was co-transfected to normalize transfection efficiencies. p NOL7 depletion suppressed the PI3K/AKT/ERK signaling pathway through inhibiting the AKT and ERK phosphorylation and activating GSK3β. See Supplementary Fig. S10a, b for quantification. q Dramatically reduced tumor growth in nude mice injected with NOL7-knockout cells, compared with that in the control group. Representative images of tumors are shown on the right. r NOL7 knockout strongly decreased the number of lung metastatic nodules. Representative photographs of pulmonary tumor metastases are shown on the right. s Schematic illustration displays the mechanism of NOL7 promoting melanoma tumorigenesis and metastasis. Throughout the figure, data are presented as mean ± s.d. (n ≥ 3); p values are calculated using the t test