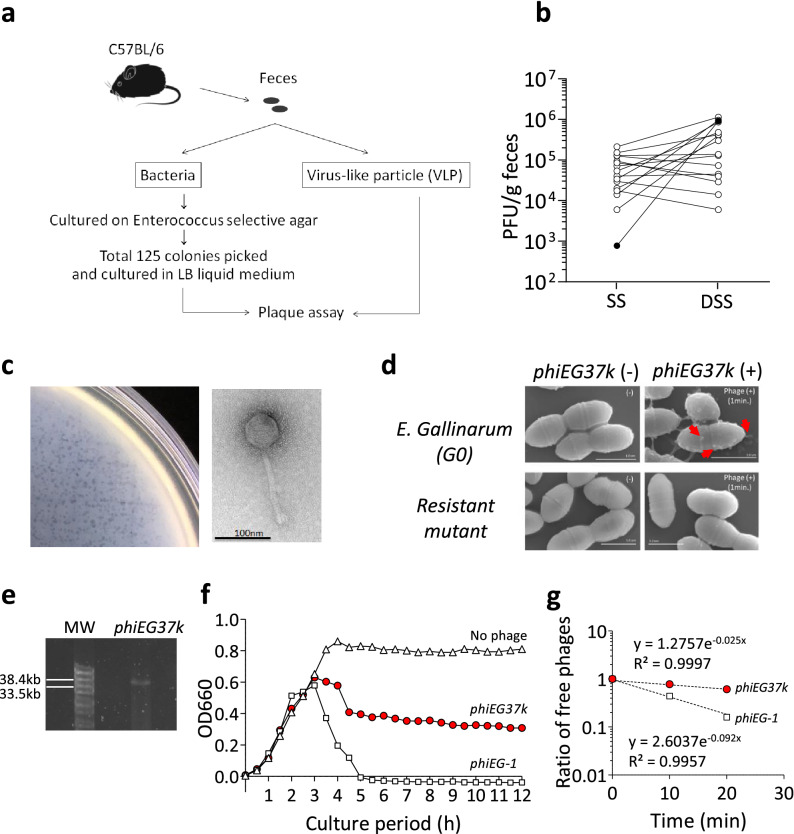
Figure 1.
Identification of novel Enterococcus phages associated with colitis. Colitis-associated Enterococcus phages were identified by screening feces from C57BL/6 mice using a plaque assay. (a) Schema of screening for gut Enterococcus phages from C57BL/6 mice in steady state. (b) Plaque-forming unit (PFU) of phages associated with 16 individual Enterococcal bacterial clones was measured in steady state (SS) and during dextran sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. The feces during colitis was taken on day 10, which is 3 days after the replacement of DSS with normal drinking water. The PFUs of the phage associated with Enterococcus strain G0 (phiEG37k) are indicated with black circles. (c) Plaques formed by phiEG37k phage (left panel) and the transmission electron microscopic image of the phage (right panel). (d) Scanning electron microscopic images of interaction of phiEG37k with host E. gallinarum or a resistant strain derived of the original strain. phiEG37k phages attached to the E. gallinarum are indicated by red arrows. Scale bars indicate 1 µm. (e) Electrophoresis of phiEG37k genome DNA on 1% agarose gel. MW; molecular weight marker (f) Lysis curves of E. gallinarum co-cultured with phiEG37k or phiEG-1, or without phage. The OD660 was measured on indicated time points. (g) Adsorption assay of phiEG37k and phiEG-1.