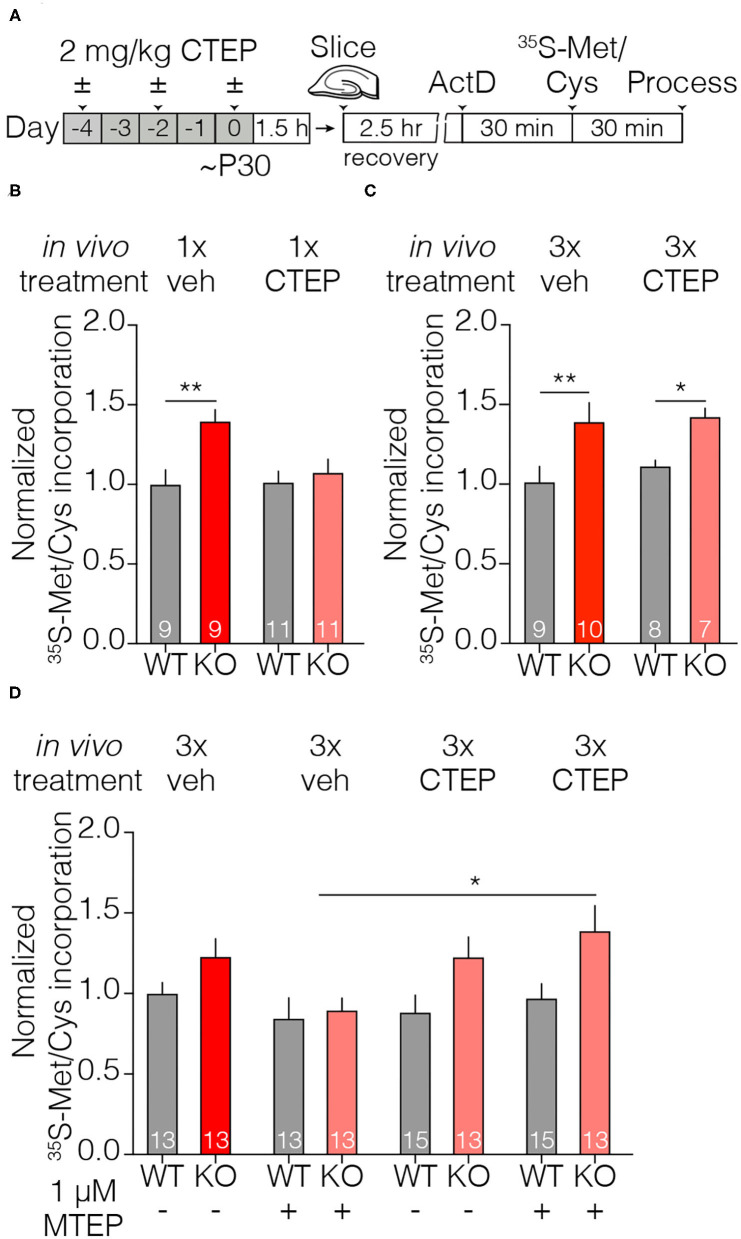
Figure 4.
Acute but not chronic CTEP treatment ameliorates elevated basal protein synthesis rates in Fmr1-KO hippocampal slices. (A) Schematic shows acute and chronic CTEP dose schedules and hippocampal metabolic labeling experimental design. (B) Basal protein synthesis rates are increased in hippocampal slices prepared from Fmr1-KO mice compared to wildtype littermate animals and acute in vivo treatment with 2 mg/kg CTEP restores Fmr1-KO protein synthesis rates to wildtype levels. There was a statistically significant effect of genotype [two-way ANOVA, F(1, 36) = 8.341, p = 0.0066] and a significant interaction between genotype and treatment. [two-way ANOVA, F(1,36) = 4.501, p = 0.0408; Šídák’s multiple comparisons test: wild type 1x vehicle vs. Fmr1-KO 1x vehicle p = 0.0036, wild type 1x CTEP vs. Fmr1-KO 1x CTEP p = 0.8183). (C) Chronic (3 doses over 5 days) in vivo treatment with 2 mg/kg CTEP has no effect on radiolabel incorporation in hippocampal slices from wildtype or Fmr1-KO animals. There was a statistically significant effect of genotype [two-way ANOVA, F(1, 30) = 15.13, p = 0.0005; Šídák’s multiple comparisons test: wild type 3x vehicle vs. Fmr1-KO 3x vehicle p = 0.0082, wild type 3x CTEP vs. Fmr1-KO 3x CTEP p = 0.0410]. (D) Bath application of 1 μM MTEP reduces elevated basal protein synthesis rates in Fmr1-KO hippocampal slices to wild type levels but has no effect on hippocampal slices from animals injected with chronic (3 doses over 5 days) 2.0 mg/kg CTEP. There was a statistically significant effect of genotype [three-way ANOVA, F(1, 50) = 8.013, p = 0.0067] and a significant interaction between in vivo treatment and in vitro treatment. [three-way ANOVA, F(1, 50) = 8.536, p = 0.0052; Šídák’s multiple comparisons test: Fmr1-KO 3x vehicle + MTEP vs. Fmr1-KO 3x CTEP + MTEP p = 0.0347). Data are displayed as mean ±SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.