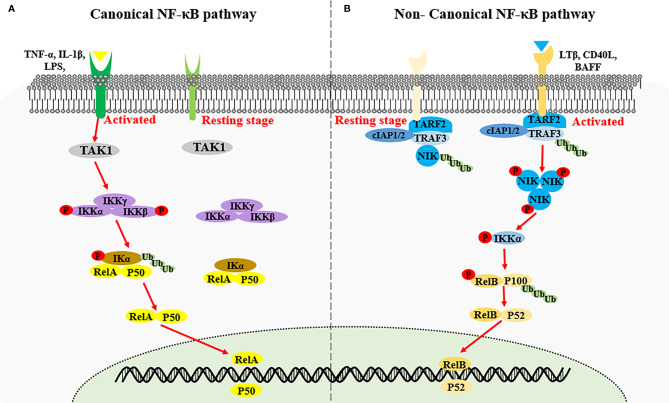
Figure 1.
Activation of canonical NF-κB signaling and non-canonical NF-κB signaling. (A) Canonical NF-κB signaling is stimulated by proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α and LPS, inducing the activation of IKK complex by TAK1. The IKK complex then phosphorylates the IκB kinase α/β (IKKα/β), causing the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of κB inhibitory factors (IκBs) protein, thereby triggering the nuclear transcription factor heterodimer RelA/p50. (B) Non-canonical NF-κB signaling is activated by the specific TNFR superfamily. Receptor activation induce the recruitment of TRAF3-TRAF2-cIAP1/2 receptor complex, followed by the degradation of TRAF3 via ubiquitination, resulting in the stabilization and accumulation of NIK. NIK phosphorylates IKKα which in turn phosphorate p100, triggering the ubiquitination and degradation of p100 to generate p52 and the nuclear transduction of RelB-p52 heterodimer.