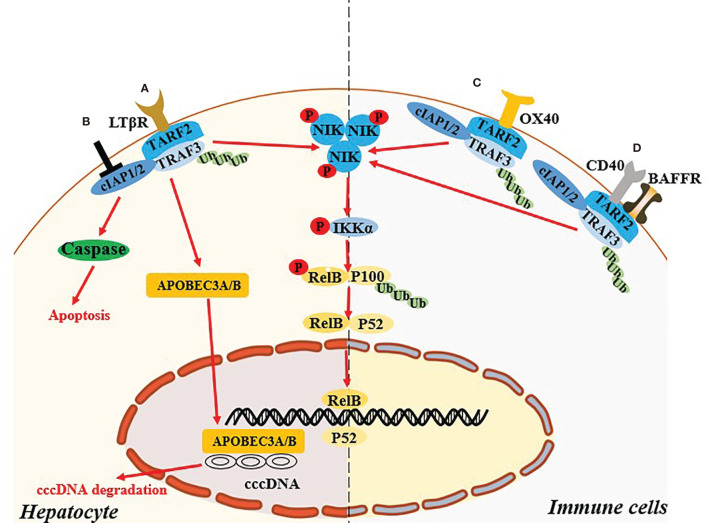
Figure 2.
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway regulates the HBV infection. (A) In hepatocyte, activation of LTB receptor in hepatocyte mediates the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway and induce the up-regulated expression of APOBCE3A/B protein, which degrade cccDNA. (B) Targeting cIAPs also mediate the activating the NIK-dependent non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway and exert the antiviral effect in hepatocyte via TNF-mediated death of infected cells. (C, D) Specific ligation of OX40, BAFFR or CD40 in immune cells might recover the exhausted immune function during HBV infection through the activation of the NIK-dependent non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway.