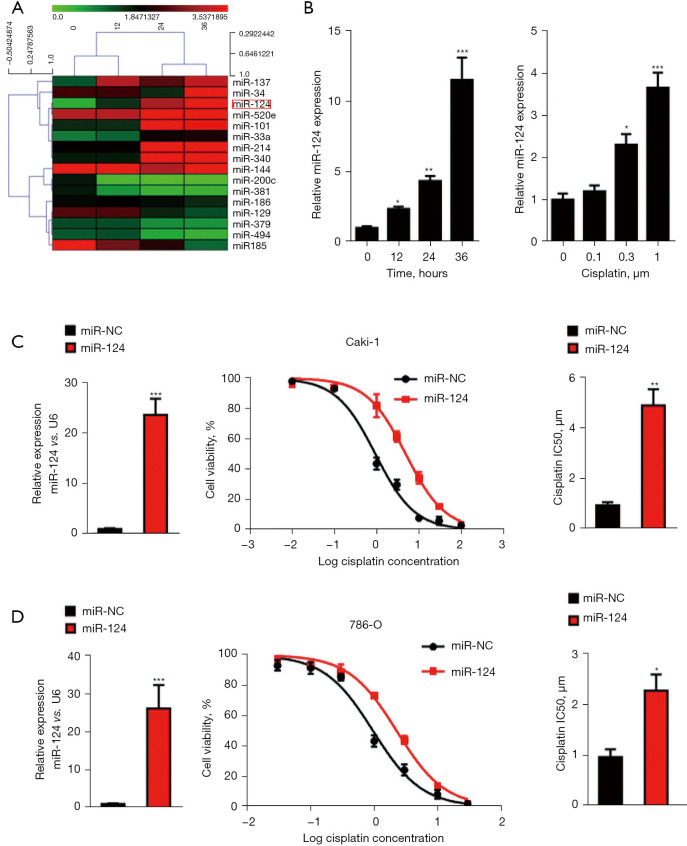
Figure 1.
MiR-124 contributed to cisplatin resistance in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells. (A) 786-O cells were treated with 10 µM cisplatin for 0, 12, 24, and 36 h. The filtered miRNA array data were used for hierarchical clustering analysis. (B) The level of miR-124 was detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). (C) The overexpression level of miR-124 in Caki-1 cells was measured by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Cell viability and half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of Caki-1 cells to cisplatin were evaluated using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. (D) The overexpression level of miR-124 in 786-O cells was measured by qPCR. Cell viability and IC50 value of 786-O cells to cisplatin were evaluated using the CCK-8 assay. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; and ***, P<0.001.