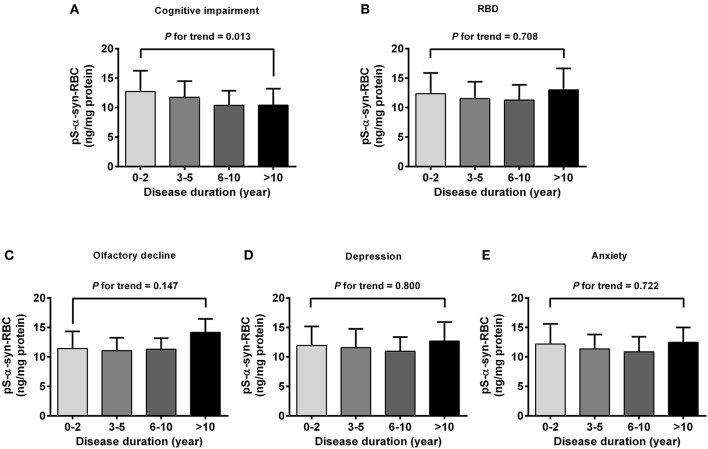
Figure 4.
Correlations of pS-α-syn-RBC with disease duration in PD patients with different non-motor subtypes. Correlations between pS-α-syn-RBC and intervals of disease duration in PD patients with non-motor subtypes was analyzed by using one-degree-freedom linear term for trend analysis. (A) Cognitive impairment; (B) RBD; (C) olfactory loss; (D) depression; (E) anxiety. p-values for the changing trend of pS-α-syn-RBC levels across increased disease durations were calculated.