Figure 1.
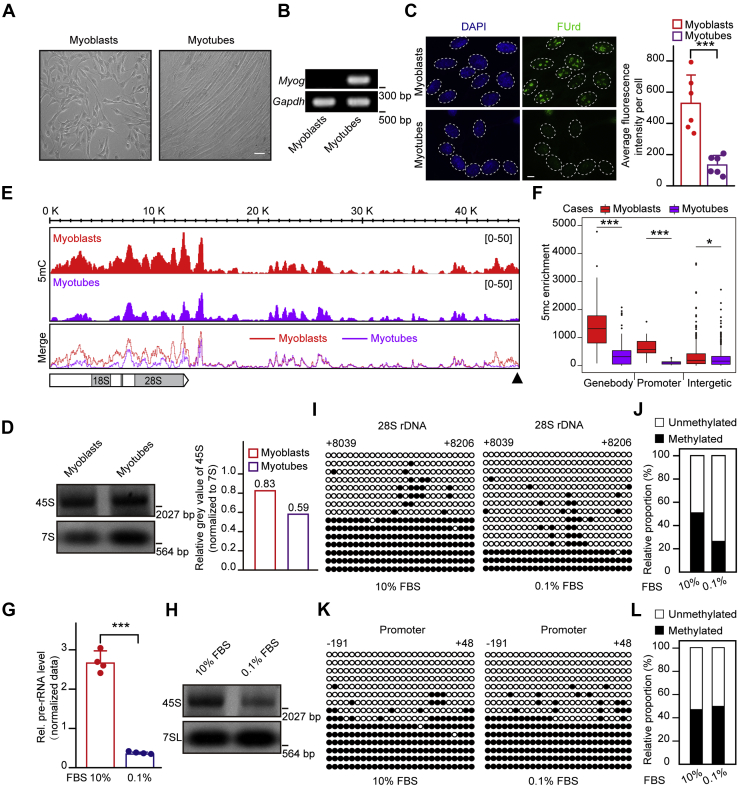
Gene body methylation is positively associated with rDNA transcription.A, morphology of C2C12 myoblasts and myotubes. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, the Myog gene is expressed in myotubes but not in myoblasts. Reverse transcription PCR assays followed by DNA gel electrophoresis showing Myog mRNA expression levels. C, Pre-rRNA synthesis is markedly reduced during differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts to myotubes. Immunostaining showing cell nuclei (blue) and FUrd (green). The pre-rRNA synthesis was measured by FUrd incorporation. Bar graph shows the average FUrd fluorescence intensity per cell of myoblasts or myotubes (n = 6). A total of 82 cells were subjected to statistics. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Scale bar, 5 μm. D, northern blotting shows the level of 45S pre-rRNA during C2C12 myoblasts differentiation. 7S RNA served as a loading control. Relative gray value of 45S band was measured by the Image J software normalizing to 7S RNA band. E, gene body and promoter methylation levels are markedly decreased upon the differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. MeDIP-Seq profiles in C2C12 myoblasts and differentiated myotubes in rDNA repeats are displayed. The horizontal bar graph on the bottom left indicates gene body regions for pre-rRNA transcripts, and the black triangle on the bottom right represents the rDNA promoter region. F, statistical analysis for MeDIP-seq results in (E). ∗p < 0.1, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, Wilcoxon test. G, RT-qPCR assays showing levels of pre-rRNA in HEK293T cells cultured in medium containing 10% FBS (normal) and 0.1% FBS (serum-starved). The cycle threshold (Ct) of 45S pre-rRNA was normalized with GAPDH. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. H, northern blotting shows the level of 45S pre-rRNA upon serum starvation. 7SL RNA served as a loading control. HEK293T cells cultured in medium containing 10% FBS (normal) and 0.1% FBS (serum-starved). I, rDNA gene body methylation levels decrease during serum starvation. Bisulfite sequencing showing the rDNA gene body methylation status in HEK293T cells cultured in medium containing 10% FBS (normal) and 0.1% FBS (serum-starved). The black and white circles represent corresponding CpG sites in rDNA gene bodies, denoting methylated and unmethylated CpG sites, respectively. The average ratio of black sites for all colonies represents the relative DNA methylation level. Corresponding sequence is shown in Figure S1G. J, analysis for the results in (I) showing the percentage of methylated and unmethylated gene body CpG sites in HEK293T cells cultured in medium containing 10% FBS (normal) and 0.1% FBS (serum-starved). The relative proportion of unmethylation and methylation was calculated by counting the numbers of black circles (methylated CpG sites) and white circles (unmethylated CpG sites). K, genomic DNA coupled with bisulfite sequencing assays were performed to show promoter methylation levels in control (10% FBS) and serum-starved (0.1% FBS) HEK293T cells. The black and white circles represent corresponding CpG sites in rDNA gene bodies, denoting methylated and unmethylated CpG sites, respectively. The average ratio of black sites for all colonies represents the relative DNA methylation level. Corresponding sequence is shown in Figure S1H. L, analysis for the results in (K) showing the percentage of methylated and unmethylated gene body CpG sites in HEK293T cells cultured in medium containing 10% FBS (normal) and 0.1% FBS (serum-starved). The relative proportion of unmethylation and methylation was calculated by counting the numbers of black circles (methylated CpG sites) and white circles (unmethylated CpG sites). ∗p < 0.1, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, two-tailed unpaired Student's t test.