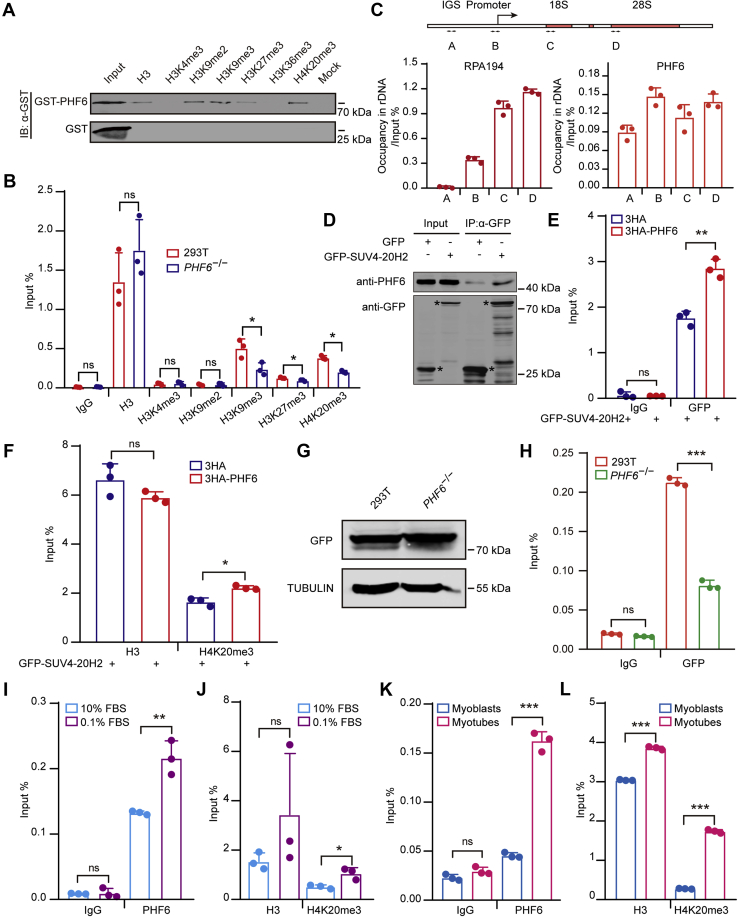
Figure 4.
PHF6 recruits SUV4-20H2 to establish H4K20me3 at gene bodies.A, PHF6 interacts with H3K9me2, H3K9me3, H3K27me3, H4K20me3 in vitro. GST-tag and GST-fused PHF6 were incubated with biotin-labeled peptides including H3, H3K4me3, H3K9me2, H3K9me3, H3K27me3, H3K36me3, H4K20me3 in vitro. Bound proteins were analyzed by the anti-GST antibody. B, the enrichment of H3K4me3, H3K9me2, H3K9me3, H3K27me3, and H4K20me3 was shown in PHF6 KO and wild-type HEK293T cells. ChIP experiments were performed using primers coated on the 28S rRNA coding region in PHF6 KO and control cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. C, a schematic of the rDNA repeat unit showing the intergenic spacer (IGS), promoter, and coding regions (upper). The arrows indicate the positions of the primers used for the following amplification. Primer sequences are listed in Table S1. PHF6 binds to different regions of the rDNA repeat unit (bottom). ChIP assays were performed in HEK293T cells using the previously annotated primers, showing the occupancies of PHF6 and Pol I (RPA194) on the rDNA repeat unit. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. D, PHF6 directly interacts with SUV4-20H2. GFP-fused full-length SUV4-20H2 plasmids were overexpressed in HEK293T cells, and whole-cell extracts were subsequently incubated with GFP beads. The pulled-down proteins were detected by anti-PHF6 and anti-GFP antibodies. E, PHF6 facilitates the binding of SUV4-20H2 to rDNA gene bodies. ChIP experiments were performed using primers coated on the 28S rDNA coding region in HEK293T cells expressing GFP-tagged SUV4-20H2 and HA-tagged PHF6 or control vector. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. F, PHF6 upregulation leads to the elevated enrichment of H4K20me3 at gene bodies. ChIP experiments were performed using primers coated on the 28S rDNA coding region in HEK293T cells expressing GFP-tagged SUV4-20H2 and HA-tagged PHF6 or control vector. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. G, GFP-SUV4-20H2 plasmids were transfected transiently into wild-type (WT) and PHF6 knockout (PHF6−/−) cells as shown by western blotting. TUBULIN served as a loading control. H, the gene body occupancy of GFP-SUV4-20H2 significantly decreases in PHF6 knockout cells. ChIP assays were performed using primers coated on the 28S rDNA coding region in HEK293T and PHF6 knockout cells. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. I, the gene body occupancy of PHF6 markedly increases upon serum deprivation. ChIP assays were performed using primers coated on the 28S rDNA coding region in HEK293T cells cultured in medium containing 10% FBS (normal) and 0.1% FBS (serum-starved). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. J, the gene body enrichment of H4K20me3 markedly rises following serum deprivation. ChIP assays were performed using primers coated on the 28S rRNA coding region in HEK293T cells cultured in medium containing 10% FBS (normal) and 0.1% FBS (serum-starved). Data are presented as the mean ± SD. K, PHF6 occupancy at gene bodies elevates during C2C12 myoblast differentiation. ChIP assays were performed using primers coated on the 28S rDNA coding region in myoblasts and myotubes. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. L, H4K20me3 enrichment at gene bodies is augmented during C2C12 myoblast differentiation. ChIP assays were performed using primers coated on the 28S rRNA coding region in myoblasts and myotubes. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.1, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, two-tailed unpaired Student's t test.