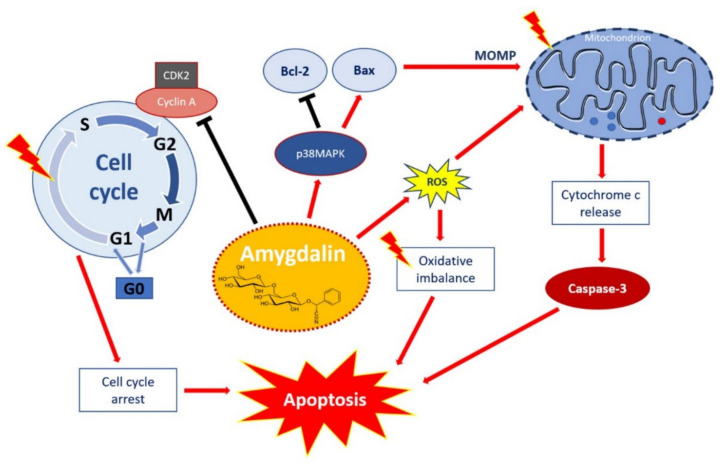
Figure 2.
Apoptotic effect of amygdalin via multiple cellular signaling pathways. Amygdalin activates p38MAPK, which affects the death stimuli, activates Bax apoptotic proteins, and inhibits Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins. Apoptosis-related proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), a decisive event in the process of cytochrome c release. Activation of the release of cytochrome c as a mitochondrial response to proapoptotic stimuli via the mitochondrial or intrinsic apoptotic pathway ultimately leads to the activation of caspases, including caspase-3, which induces apoptosis. Amygdalin induces ROS overproduction, which compromises the oxidative balance and eventually leads to apoptosis. Amygdalin downregulates cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) and cyclin A, which induces cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phases. Amygdalin also inhibits cell transfer from the G1 to S phase, resulting in the inhibition of cell proliferation and growth. “Activation” is shown by red arrows and ‘inhibition’ shown by black arrows. Taken from Pharmaceuticals with permission of authors [51].