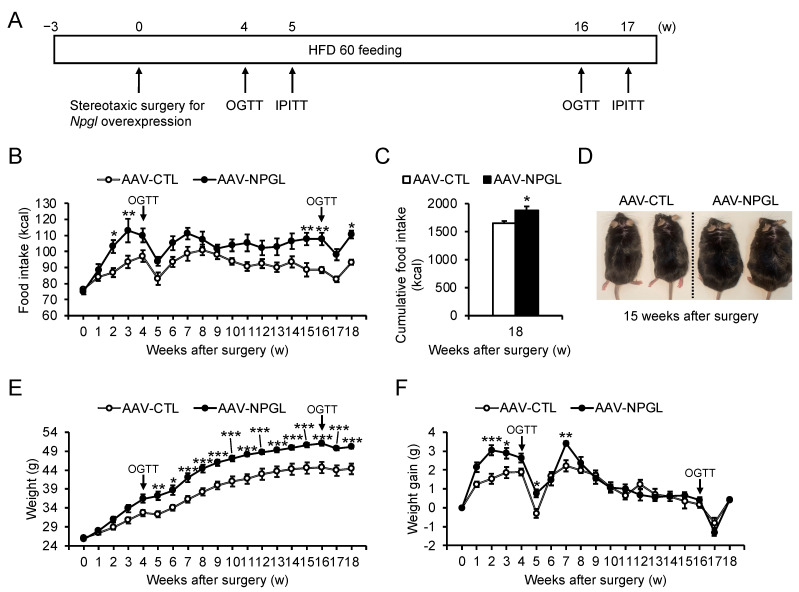
Figure 1.
Effects of Npgl overexpression on weight gain and food intake in mice fed a high-fat diet with 60% calories from fat (HFD 60). These mice were injected with an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector, either a control (AAV-CTL) or a vector carrying the NPGL precursor gene (AAV-NPGL). (A) Experimental procedure. Mice were subjected to the first oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and the first intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test (IPITT) at 4 and 5 weeks after surgery, respectively. Thereafter, mice were subjected to the second OGTT and IPITT at 16 and 17 weeks after surgery, respectively. (B,C) Weekly (B) and (C) cumulative food intake over 18 weeks. (D) Representative photograph of mice placed on HFD 60 at 15 weeks after injection of AAV-CTL or AAV-NPGL. (E) Weight. (F) Weekly weight gain. Statistical analyses were performed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s test (B,E,F) or Student’s t-test (C). Each value represents the mean ± standard error of the mean (AAV-CTL: n = 8, AAV-NPGL: n = 8; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005).