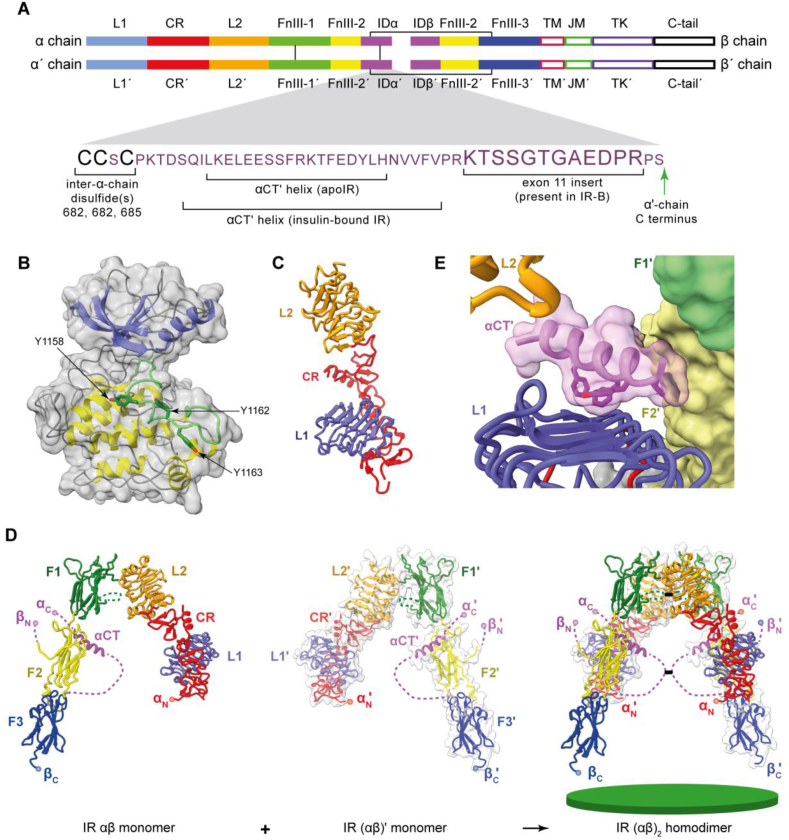
Figure 2.
Three-dimensional structure of the human apo insulin-receptor (IR) ectodomain. (A) Domain layout of the disulfide-linked (αβ)2 homodimer; close-up view shows the sequence detail of the α chain's C-terminal region. The domain nomenclature is defined in the main text. Interchain disulfide bonds are shown as green lines. (B) Bi-lobal structure of the IR TK domain (N-terminal lobe in blue, C-terminal lobe in yellow, and the activation loop in green). (C) Structure of the IR L1-CR-L2 module. (D) Structure of the αβ monomer showing its pairing with the (αβ)′ monomer to form the (αβ)2 homodimer. The green disc (bottom right) represents the cell membrane. In the panel, the N and C termini of the α chain and β chain are denoted as αN, αC, βN, and βC, respectively. Dashed connectors indicate residue segments disordered in the crystal structure. (E) Detail of the engagement of the αCT′ helix with the L1-β2 surface. Panels are based on PDB 1IRK [92], PDB 2HR7 [7] and PDB 4ZXB [95].