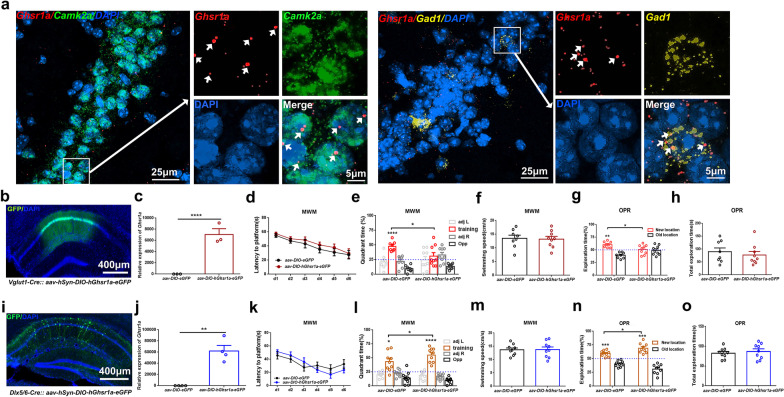
Fig. 1.
Selective GHS-R1a upregulation in dCA1 pyramidal neurons or interneurons has opposite effect on hippocampus-dependent memory encoding. a Representative fluorescent in situ hybridization images showing endogenous Ghsr1a expression in both excitatory and inhibitory dCA1 neurons of C57BL/6J mice. Ghsr1a (red), Camk2a (green), Gad1 (yellow), DAPI (blue). Arrowheads (white) indicate Ghsr1a signals within Camk2a- or Gad1-expressing neurons. b, i Representative fluorescent images of dorsal hippocampus taken 4 weeks after virus injection. Vglut1-Cre mice (b), Dlx5/6-Cre mice (i). GFP (green), DAPI (blue). c, j RT-qPCR analyses showing increased hGhsr1a expression in dorsal hippocampus 4 weeks after delivery of hGhsr1a-expressing virus. Vglut1-Cre mice (c), n = 3 per group; Dlx5/6-Cre mice (j), n = 4 per group. d–h, k–o Learning and memory performance. Vglut1-Cre mice (d–h), Dlx5/6-Cre mice (k–o). d–f, k–m Morris water maze assays. d, k GHS-R1a upregulation does not affect spatial learning. e, l Spatial memory tested 24 h after the 6th day training. Elevated GHS-R1a in excitatory neurons impairs spatial memory (e), while increased GHS-R1a expression in inhibitory neurons enhances spatial memory (l). f, m Averaged swimming speed during probe test. g, h, n–o Object-place recognition (OPR) assays. g Cre-dependent GHS-R1a upregulation in excitatory neurons impairs OPR memory. n Cre-dependent GHS-R1a upregulation in inhibitory neurons improves OPR memory. h, o Total object exploration time during OPR test. Vglut1-Cre mice with GHS-R1a-expressing virus (n = 9), Vglut1-Cre mice with control virus (n = 8), Dlx5/6-Cre mice, n = 9 per group. All data is shown as means ± SEM. Two-way repeated-measure ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test for (d, e, g, k, l, n), unpaired t test for (c, f, h, j, m, o), ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, ** P < 0.01 or *P < 0.05 means significant difference, n.s. means no significance