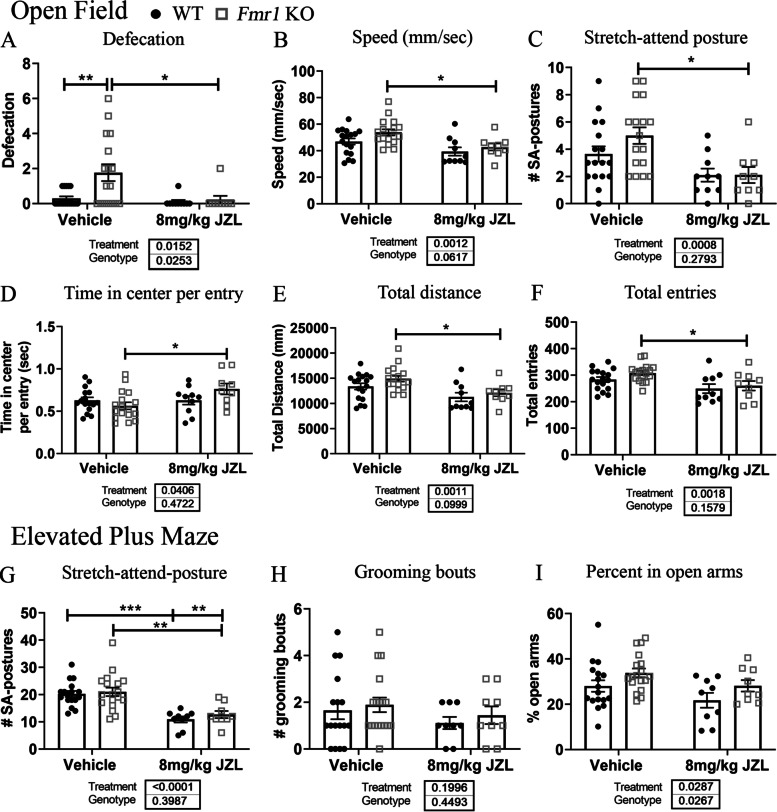
Fig. 6.
JZL-184 treatment improves anxiety/hyperactivity phenotype associated with Fmr1 KO mice. Graphs show behavioral measures assessed for anxiety-like behaviors and hyperactivity in the open field and elevated plus maze 4 h post-treatment in Fmr1 KO and WT mice. Behavioral measures assessed in the open field included the amount of defecation (A), speed (mm/s) (B), number of stretch-attend (SA) postures (C), time in the center per entry (D), total distance (E), and total entries. G–I Graphs show EPM behaviors assessed, including the number of stretch-attend postures (G), grooming bouts (H), and percent time spent in open arms (I). Statistical analysis was performed using the two-way ANOVA for all comparisons. Values represent means per group, and error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. WT vehicle, N = 17; Fmr1 KO vehicle, N = 17–18; WT 8 mg/kg JZL-184, N = 9–10; Fmr1 KO 8 mg/kg JZL-184, N = 9. Excluded: WT vehicle, N = 1 (D), Fmr1 KO vehicle, N = 1 (OF); WT 8 mg/kg JZL-184, N = 1 (EPM)