Figure 2.
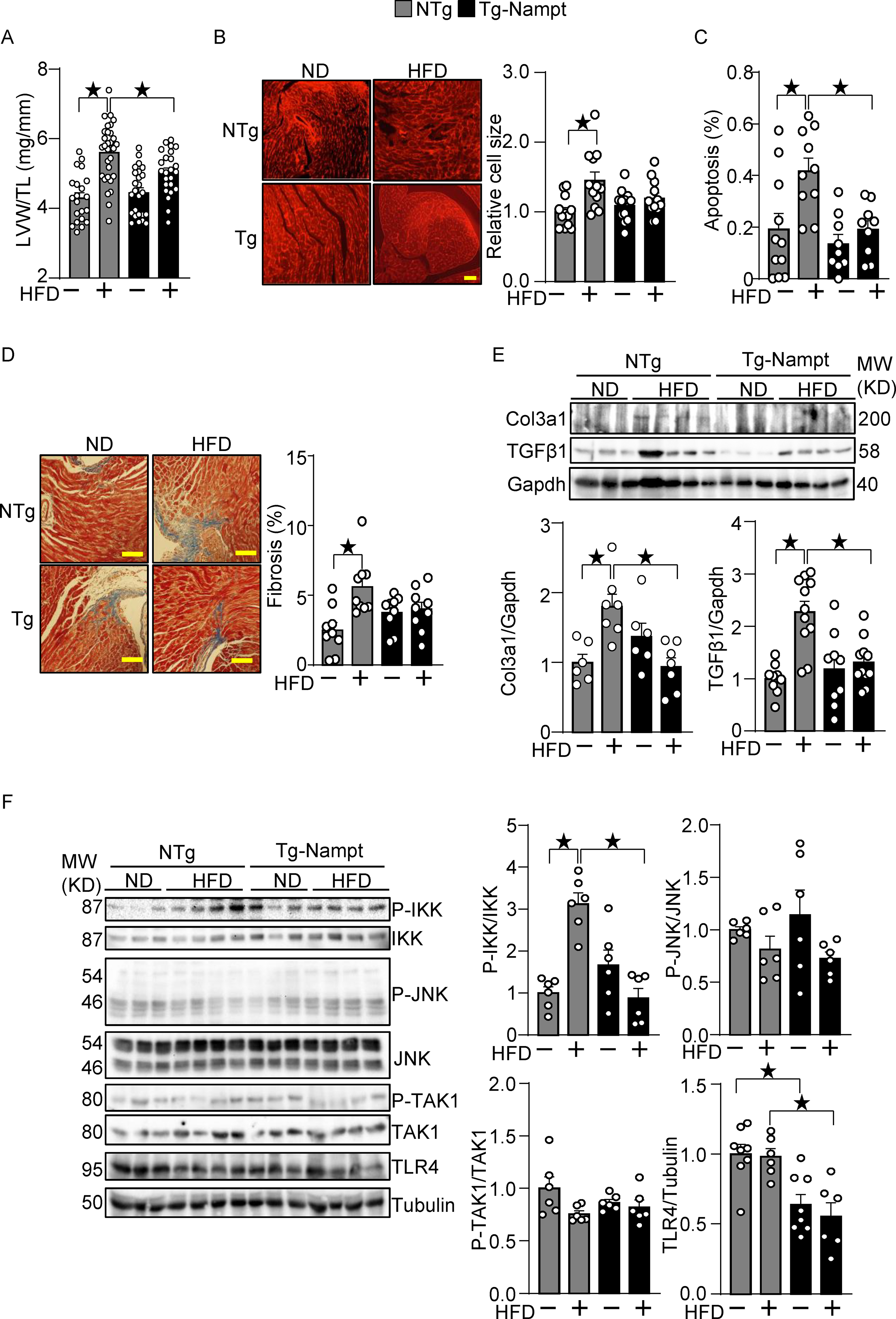
Nampt overexpression ameliorates HFD-induced cardiac pathologies relevant to diastolic dysfunction. (A-B) Nampt ameliorates HFD-induced left ventricular (LV) (A) and cardiomyocyte (B) hypertrophy. (A) LV hypertrophy indicated by LV weight (LVW)/tibial length (TL). (B) Relative cell size was evaluated, using wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining. (C) Nampt ameliorates HFD-induced apoptotic cell death. TUNEL-positive cells (apoptotic cells) were quantified as the number of TUNEL-positive/total number of nuclei (%). (D) Nampt ameliorates HFD-induced cardiac fibrosis. Cardiac fibrosis was evaluated using Masson’s trichrome staining. (Left) Representative images from each group are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm. (Right) Quantitative analysis of the fibrotic areas. (E) Nampt inhibits HFD-induced fibrosis markers. (F) Nampt inhibits HFD-induced IKK activation. Heart lysates were prepared from NTg and Tg-Nampt mice after 3 months of HFD feeding. Indicated pro-inflammatory signal regulators were examined with Western blot analyses. Statistical significance was determined with ANOVA (A, B, C, E and F (P-JNK/JNK, P-TAK1/TAK1 and TLR4/Tubulin)) and the Kruskal-Wallis test (D, F (P-IKK/IKK)).
