Figure 8.
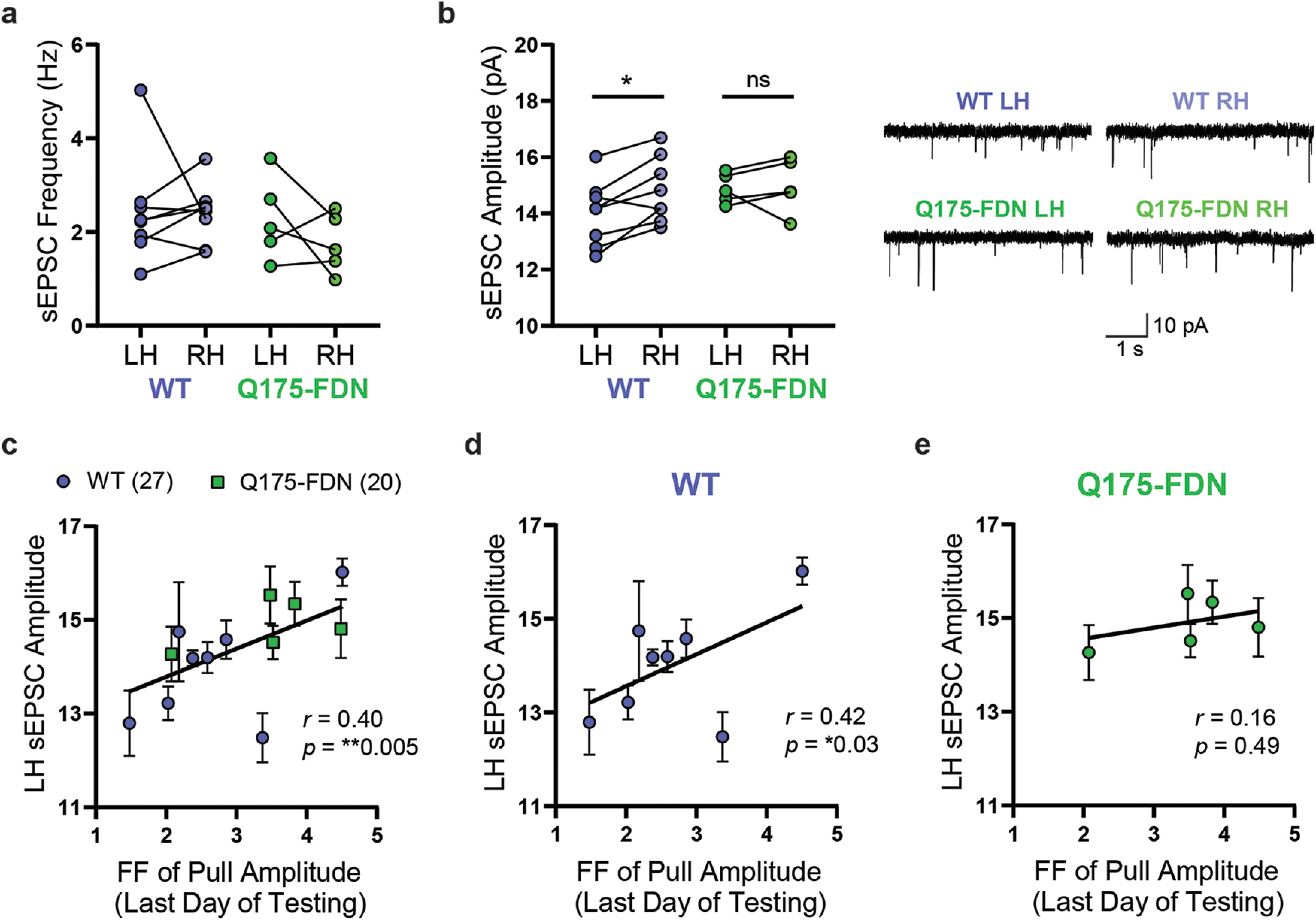
PiPaw training is associated with a decrease in average DLS-MSN sEPSC amplitude in the hemisphere contralateral to the trained forelimb in WT, but not Q175-FDN mice. a, The average frequency of sEPSCs in DLS-MSNs was not significantly different between left and right hemisphere in PiPaw-trained WT and Q175-FDN mice (n = 8 WT, 5 Q175-FDN). Lines indicate paired values for each mouse. b, Average sEPSC amplitude in DLS-MSNs was significantly lower in the left hemisphere (contralateral to the trained forelimb) compared with the right hemisphere in WT animals (n = 8), but no hemispheric differences were seen in Q175-FDN mice (n = 5). Lines indicate paired values for each mouse. Right, Representative traces. c, Average sEPSC amplitude in the left hemisphere (contralateral to the trained forelimb) was significantly correlated with the Fano factor of pull amplitude on the last day of testing across WT and Q175-FDN mice (n = 13 mice, 47 cells). d, LH sEPSC amplitude was correlated with the Fano factor of pull amplitude on the last day of testing in WT mice (n = 8 mice, 27 cells). e, LH sEPSC amplitude was not correlated with the Fano factor of pull amplitude on the last day of testing in Q175-FDN mice (n = 5 mice, 20 cells).
