Figure 3.
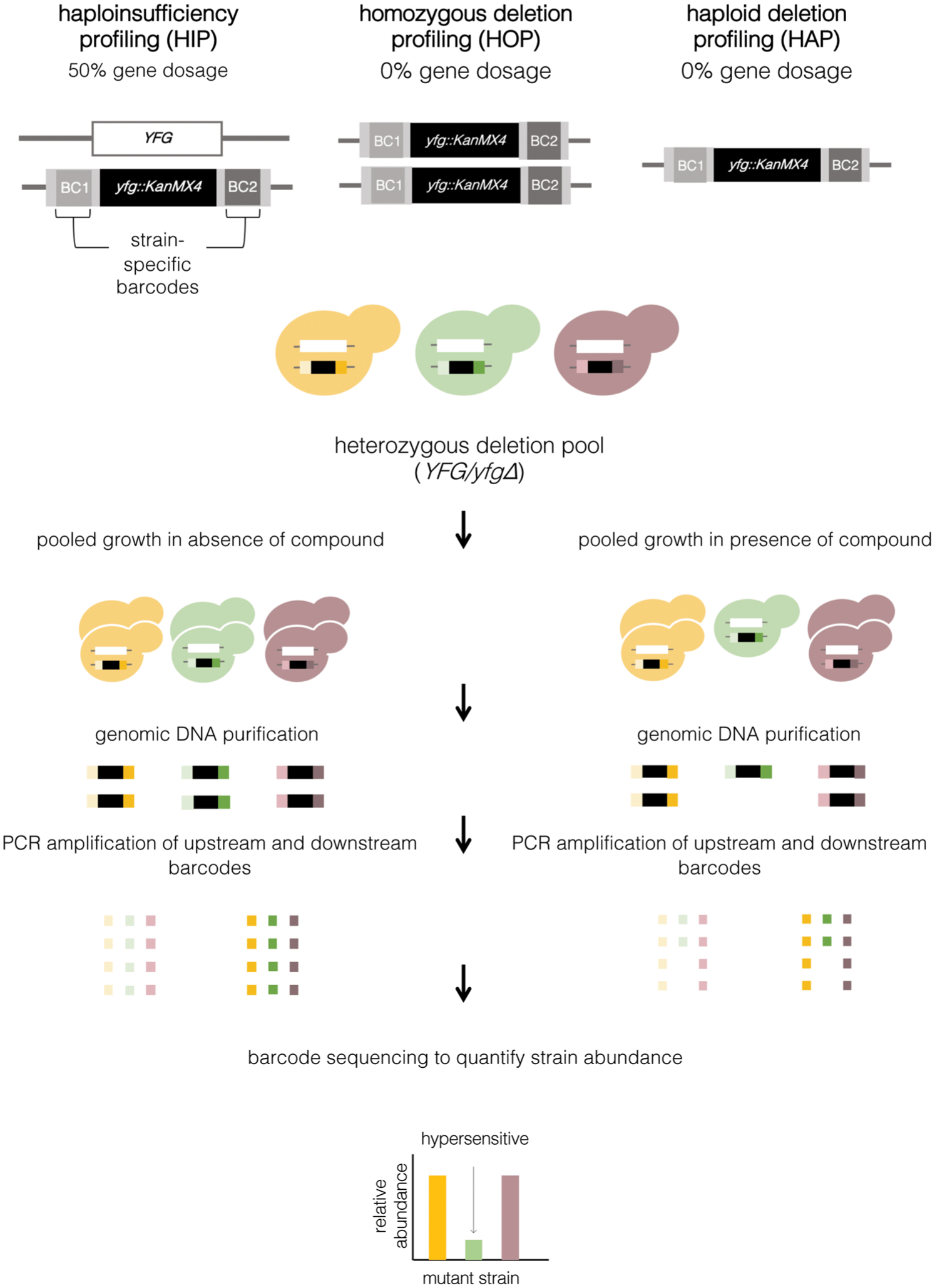
Reduced gene dosage chemical-genomic assays. Haploinsufficiency profiling (HIP), homozygous deletion profiling (HOP), and haploid deletion profiling (HAP) operate under a common principle. HIP employs heterozygous deletion mutants of essential or nonessential genes in a diploid for reduced gene dosage. HOP utilizes homozygous deletion mutants in a diploid parent and HAP utilizes haploid deletion mutants generated in a haploid parent to abolish the expression of nonessential genes. Individual strains within each genome-wide library are tagged with two unique DNA barcodes, upstream and downstream (BC1 and BC2), that permit simultaneous analysis within a single pool. Deletion libraries are grown competitively in the absence and presence of a compound of interest. Genomic DNA is isolated after a duration of pooled growth, and PCR amplification of strain-identifying barcodes is performed using universal primers for the upstream or downstream barcodes. High-throughput barcode sequencing and normalization to the untreated pool is used to quantify strain representation.
