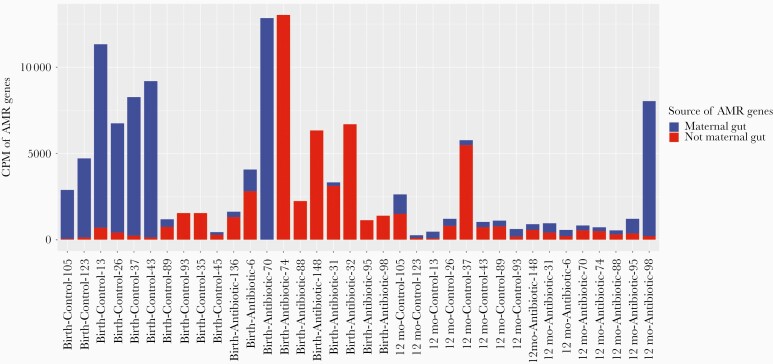
Figure 4.
Antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) gene abundance and source of AMR genes in infants’ gut microbiome. The unit of abundance unit is copies per million (the number of reads mapped to the AMR gene per million reads mapped to all genes in the sample). AMR genes in infants transmitted from mothers are not necessarily exclusively shared genes (as listed in Table 1); exclusively shared genes must exist in both mother and infant and must be 100% identical in full gene length. In this figure, an AMR gene in an infant’s sample is considered transmitted if the gene is from a species that can be traced back to the mother’s sample, even if the AMR gene was not found in the mother’s sequencing data.