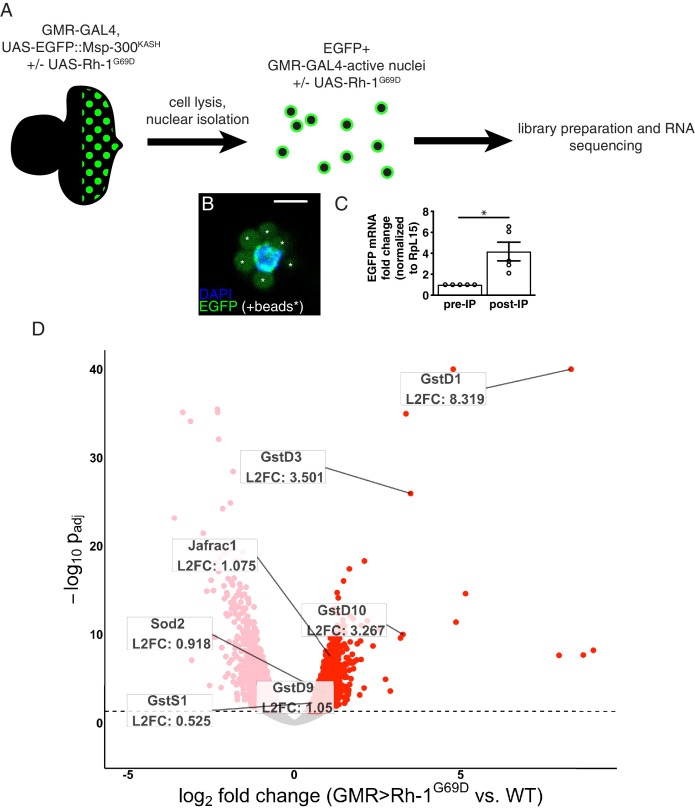
Figure 1. RNA-sequencing reveals upregulation of antioxidant genes in response to ER stress.
(A) Workflow for isolation of tagged nuclei from eye imaginal discs and preparation of total RNA for transcriptional profiling. (B) A representative image of an isolated, EGFP-tagged nucleus. Asterisks label auto-fluorescent anti-EGFP-coupled beads. Scale bar = 5 µm. (C) Representative qRT-PCR of pre- and post-isolation disc nuclei showing a significant enrichment of EGFP mRNA following isolation. The error bar represents standard error (SE). Statistical significance was assessed through a two tailed t-test. * = p < 0.05. (D) Volcano plot of genes differentially expressed in the presence or absence of Rh1G69D expression. Genes significantly up/downregulated in response to Rh1G69D are shown in red and pink, respectively. A select set of antioxidant genes induced by Rh1G69D are labeled with their log2 fold change values. Note: -log10 padj of gstD1 exceeded the bounds of the graph (180) and was constrained to the maximum displayed value of 40 for readability.