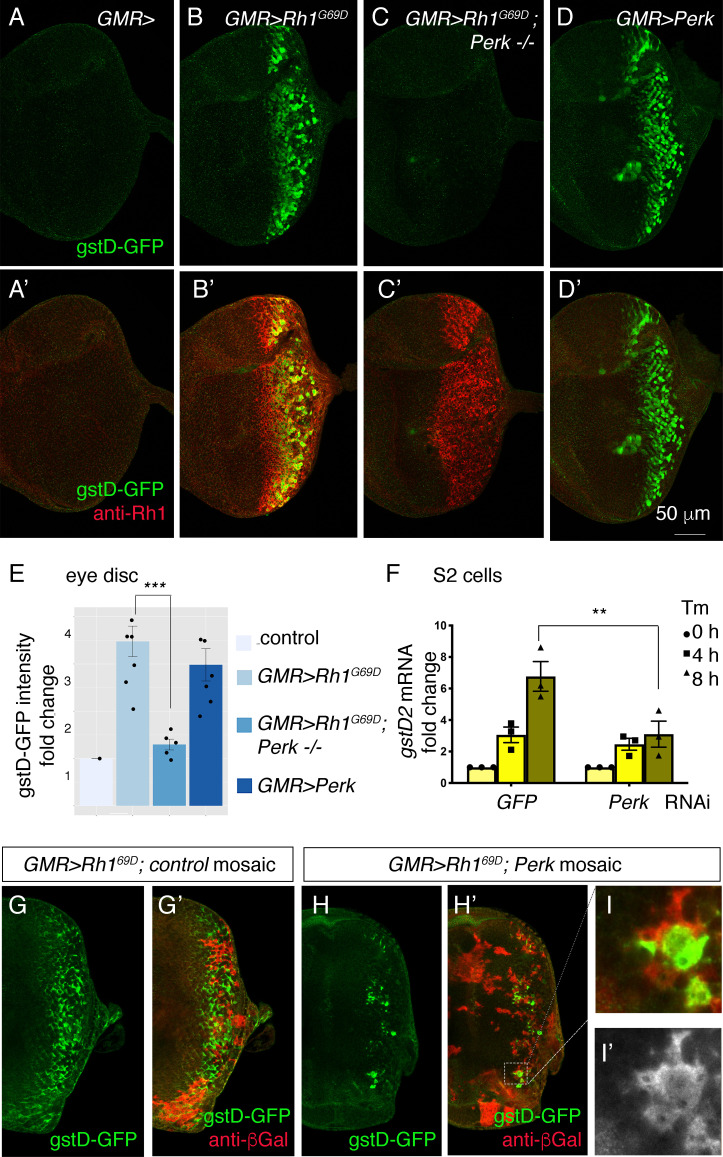
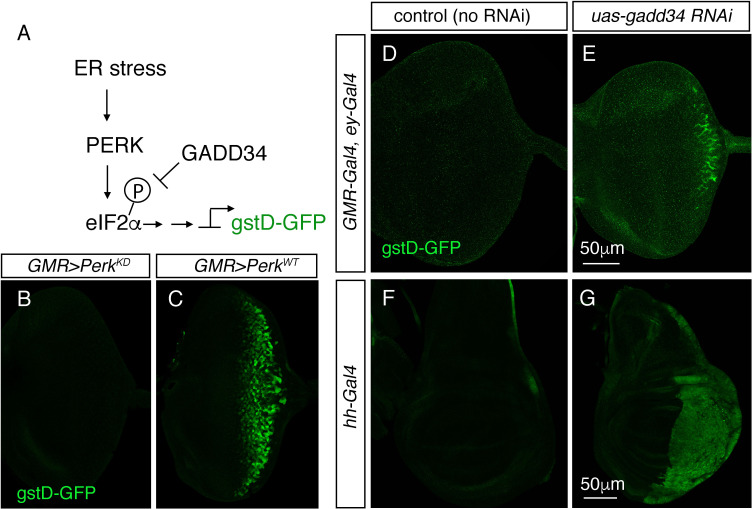
Figure 3. Perk is necessary and sufficient to induce gstD-GFP expression.
(A–D) Representative eye imaginal discs with gstD-GFP (green) alone channels (A–D), and gstD-GFP (green) channels merged with anti-Rh1 (red) (A’-D’). The genotypes of the discs are as follows: (A) GMR-Gal4; gstD-GFP/+, (B) GMR-Gal4; gstD-GFP/UAS-Rh1G69D, (C) GMR-Gal4; gstD-GFP/UAS-Rh1G69D; Perke01744 (D) GMR-Gal4; gstD-GFP/UAS-Perk. (E) Quantification of gstD-GFP pixel intensity fold change from posterior eye discs of the indicated genotypes from A-D. (F) qRT-PCR of gstD2 normalized to RpL15 in S2 cells treated with 10 ug/mL tunicamycin for 0, 4, or 8 hr. Cells were either pre-treated with control dsRNA (GFP) or those targeting Perk. (G–I) gstD-GFP (green) containing GMR > Rh1G69D eye discs with either control mosaic clones (G), or those with Perk loss-of-function clones (H, I). Homozygous Perk e01744 clones in H’ and I are marked by the absence of β-galactosidase (red) expression. Note that gstD-GFP expression occurs broadly in the background of control mosaic clones, but is largely absent in Perk homozygous mutant clones. (I, I’) A magnified view of the dotted inset in (H’). (I’) β-galactosidase only channel (marking Perk-positive cells; in white). Scale bar = 50 μm. * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.005, *** = p < 0.001.