Figure 2.
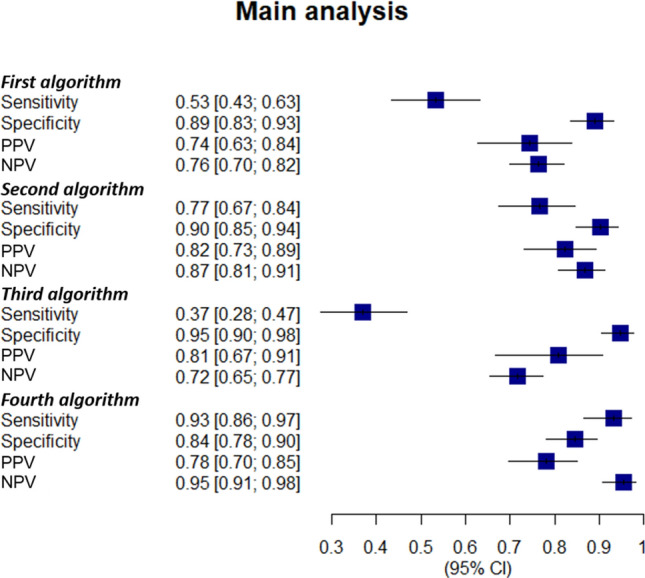
Validation of the algorithms used for selecting rheumatoid arthritis patients: the main analysis. The four algorithms were evaluated for: sensitivity (proportion of patients correctly classified as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients by the algorithm within the RA ones); specificity (proportion of patients correctly classified as without RA by the algorithm within patients without RA); positive predictive value (proportion of patients correctly classified as RA by the algorithm within all patients classified as RA by the algorithm) and negative predictive value (proportion of patients correctly classified as without RA by the algorithm within all patients classified as non-RA by the algorithm). Out of patients with the first bDMARD supply from 2014 to 2016 and at least one visit at the Rheumatology Unit of Pisa University Hospital from 2013 to the index date, the four algorithms involved the following items: (1) RA according to hospital discharge records or emergency department admissions (ICD-9 code, 714*); (2) RA according to exemption code from co-payment (006); (3) RA according to hospital discharge records or emergency department admissions (ICD-9 code, 714*) AND RA according to exemption code from co-payment (006); (4) RA according to hospital discharge records or emergency department admissions (ICD-9 code, 714*) OR RA according to exemption code from co-payment (006). bDMARD biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, 95% CI 95% confidence interval, ICD-9 international classification of diseases 9th revision, NPV negative predictive value, PPV positive predictive value, RA rheumatoid arthritis.
