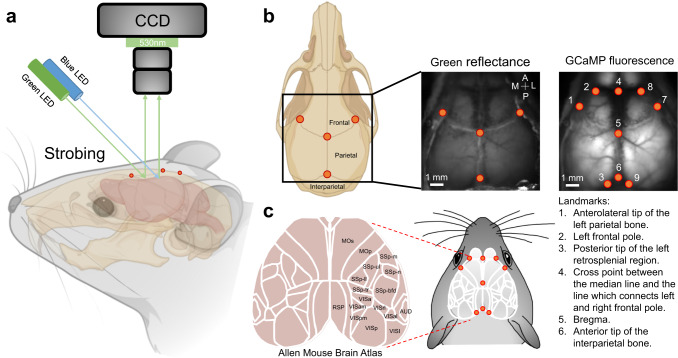
Fig. 1. Set up of wide-field calcium imaging and definition of landmarks.
a Schematic showing green (560 nm) and blue (480 nm) LED lights targeted directly above the cranial recording window that were used to illuminate the cortex. Green reflectance and emission fluorescence were filtered using a 510–550 nm bandpass filter. The mouse head and skull were created with BioRender.com. b Examples of raw GCaMP and green reflectance images are shown with annotated landmarks. c Reference atlas (white outlines; ©2004 Allen Institute for Brain Science. Allen Mouse Brain Atlas. Available from: http://mouse.brain-map.org/) used for our segmentation process. Mop, primary motor area; Mos, secondary motor area; SSp-m, primary somatosensory area, mouth; SSp-ul, primary somatosensory area, upper limb; SSp-ll, primary somatosensory area, lower limb; SSp-n, primary somatosensory area, nose; SSp-bfd, primary somatosensory area, barrel field; SSp-tr, primary somatosensory area, trunk; VISp, primary visual area; VISa, anterior visual area; VISam, anteromedial visual area; VISpm, posteromedial visual area; VISrl, rostrolateral visual area; VISal, anterolateral visual area; VISI, lateral visual area; RSP, retrosplenial area; AUD, auditory areas.