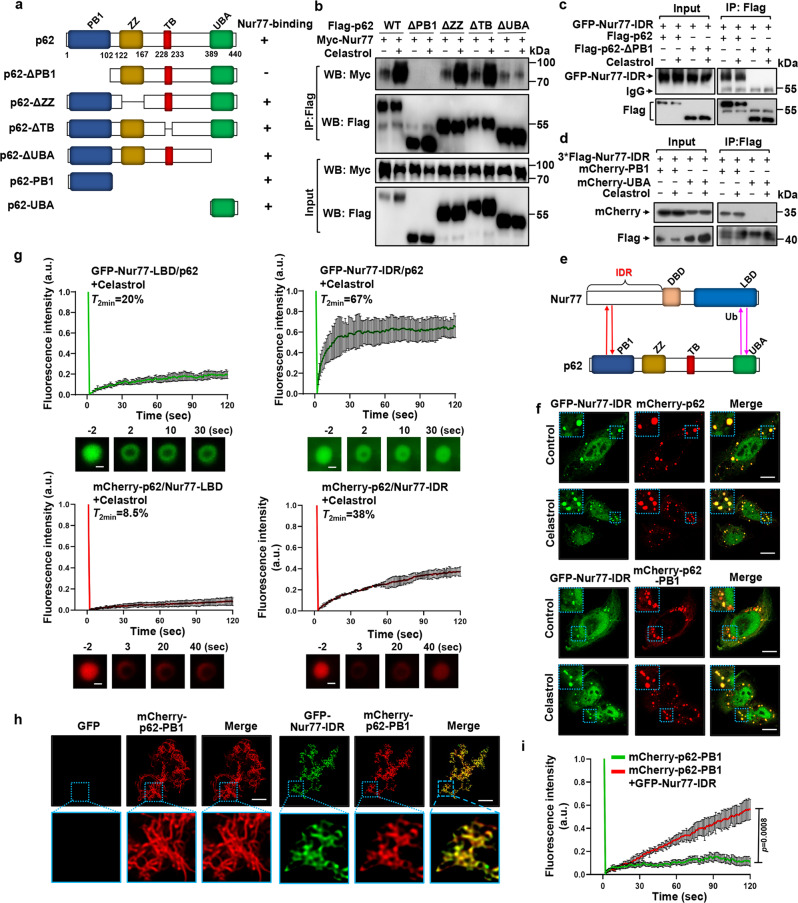
Fig. 7. IDR interaction with PB1 promotes liquidity of p62 condensates.
a Schematic representation of p62 and mutants and their interaction with Nur77. PB1 Phox/Bem1p protein-protein binding domain. ZZ zinc-finger domain, TB TRAF6 binding domain, UBA ubiquitin-associated domain. b–d Interaction of Nur77 and p62, as well as their mutants, was analyzed in HeLa cells treated with or without celastrol by co-IP assay. e Multivalent interaction between Nur77 and p62. The interaction between the IDR of Nur77 and PB1 of P62 is ligand-independent (red), whereas the interaction between LBD of Nur77 and UBA of p62 depends on celastrol that triggers Nur77-LBD ubiquitination (pink). f Immunofluorescence images showing colocalization of GFP-Nur77-IDR with mCherry-p62 or mCherry-p62-PB1 after treatment with or without celastrol. Scale bar, 10 μm. g FRAP analysis of the effect of Nur77-IDR in regulating p62 mobility in HeLa cells. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar, 1.5 μm. h Representative images showing the effect of GFP-Nur77-IDR on the filamentous structures of mCherry-p62-PB1 when mCherry-p62-PB1 was incubated with GFP or GFP-Nur77-IDR at intermediate molar ratio (1:2). Scale bar, 10 μm. i FRAP analysis of the effect of GFP-Nur77-IDR on mCherry-p62-PB1 mobility in vitro. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis, and data were presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments). Data represent at least three independent experiments. Source data are provided as Source Data file.