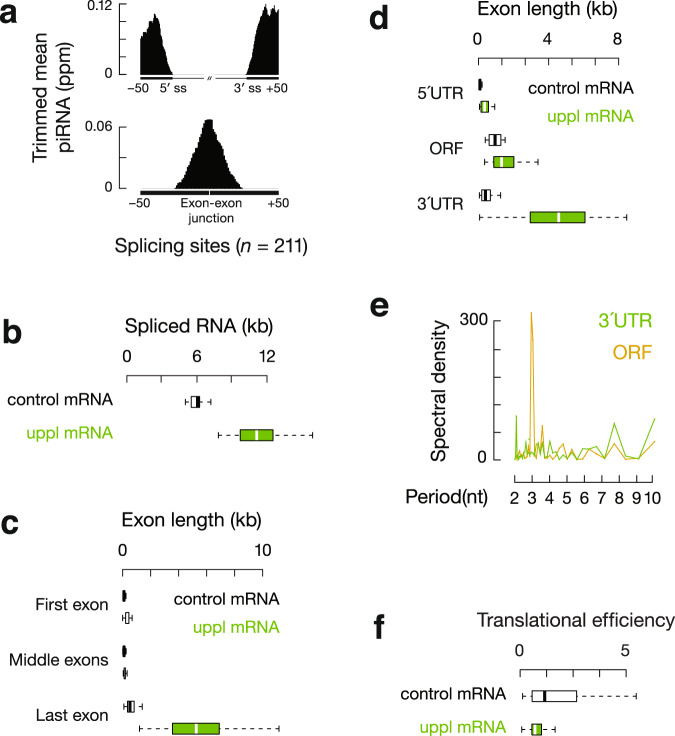
Fig. 2. Translation and piRNA processing are coupled on uppl mRNAs.
a Top, aggregation plots of piRNA reads surrounding the 5′ and 3′ splice sites of uppl mRNAs from the adult mouse testes. Bottom, the signal was calculated for non-genome matching piRNA reads mapping to exon–exon junction sequences. b Boxplots showing spliced RNA transcript length distributions. Control mRNA n = 43, uppl mRNA n = 30. c Boxplots showing exon length distributions. Control mRNA first or last exon n = 43, uppl mRNA first or last exon n = 30. Control mRNA middle exon n = 145, uppl mRNA middle exon n = 69. d Boxplots showing ORF and UTR length distributions. Control mRNA n = 43, uppl mRNA n = 30. e Discrete Fourier transformation of the distance spectrum of 5′-ends of RPFs across ORFs (gold) and 3′UTRs (green) of uppl mRNAs in adult wild-type testes. f Boxplots showing translational efficiency (RPF abundancy divided by mRNA abundancy) in adult wild-type testes. Control mRNA n = 43, uppl mRNA n = 30. Box plots in (b–d and f) show the 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers represent the 5th and 95th percentiles, and midlines show median values.