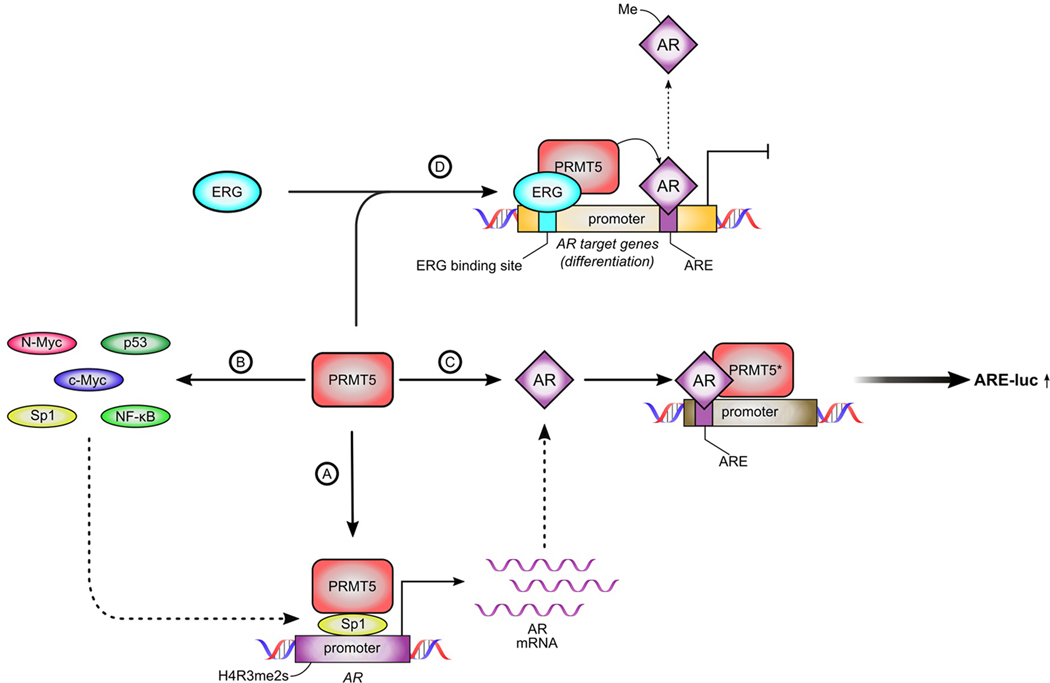
Fig. 1: Mechanisms of PRMT5-driven regulation of AR signaling in prostate cancer.
PRMT5 is implicated in the regulation of AR signaling at multiple steps: (A) PRMT5 is recruited to the AR promoter by Sp1 to symmetrically dimethylate H4R3 thus promoting AR transcription. (B) PRMT5 can modulate activity of transcriptions factors that regulate AR expression. (C) PRMT5 can function as an AR co-activator independently of its methyltransferase activity to enhance activation of AR target gene expression. (D) PRMT5 can methylate AR in an ERG-dependent manner leading to decreased recruitment of AR to AR target gene promoters of differentiation-promoting genes and increased cell proliferation. *mechanism (C) is independent of PRMT5 enzymatic activity.