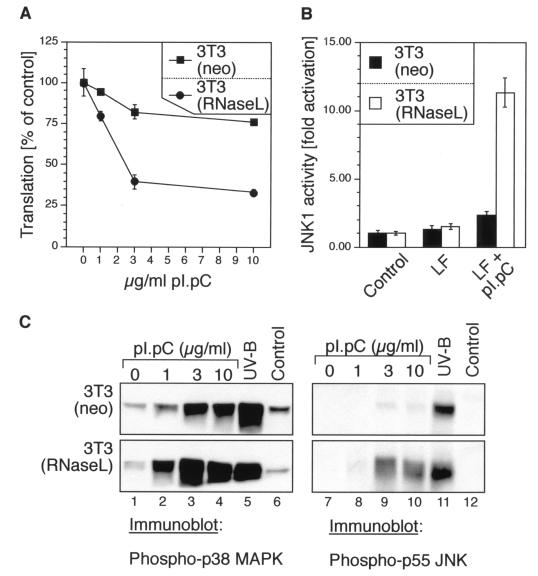
FIG. 2.
dsRNA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis, activation of JNK, and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and JNK in 3T3(neo) and 3T3(RNaseL) cells. (A) The cells were grown in 12-well plates to ∼70% confluence in normal growth medium and then leucine deprived for 1.5 h in leucine- and serum-free DMEM. Lipofectin mixes were made in leucine- and serum-free DMEM to contain 0, 1, 3, or 10 μg of pI · pC per ml and were given to the cells. Between 2.5 and 3 h after the pI · pC addition, the cells were pulse-labeled with 1 μCi of [3H]leucine per ml and processed further as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars indicate standard deviation from experimental points in triplicate determinations. (B) Immunocomplex kinase assay. The cells were grown in 10-cm-diameter plates to ∼70% confluence in normal growth medium. The growth medium was then exchanged, where indicated, with serum-free DMEM (control) or Lipofectin (LF)-containing serum-free DMEM, without or with 10 μg of pI · pC per ml. JNK activity was determined 3 h later in immunocomplex kinase assays as described for Fig. 1B. Error bars indicate standard deviation from experimental points in triplicate determinations. (C) Immunoblot analyses of p38 MAPK and JNK phosphorylation, using phosphoepitope-specific antibodies. The cells were grown and treated as for panel B with the indicated concentrations of pI · pC. For the UV-B irradiation, the cells were given a 1,200-J/m2 dose of UV-B as described previously (26) and harvested 30 min later.