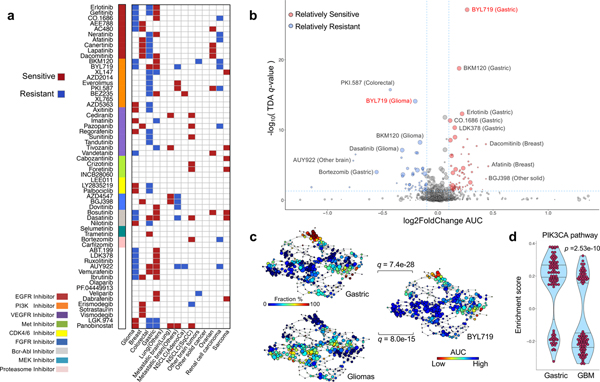
Figure 2. Therapeutic landscape of PDCs and lineage-specific responses.
(a) Tumor lineage-specific drug association identified using 60 compounds (n=462 biologically independent samples). Two-sided wilcox rank sum test was applied to determine the relative differences of drug sensitivity between specific tumor type and the rest. Only significant associations are marked (q-value < 0.05). Drugs are ordered based on their known targets. (b) A volcano plot representation of TDA analysis showing the magnitude (Fold change, x-axis) and significance (TDA q value, y-axis) of all tumor-drug associations (n=462 biologically independent samples). Each circle represents a single tumor-drug interaction and the size is proportional to the cohort size of that tumor. (c) Distribution of gastric, glioma PDCs and BYL719 drug AUC profile over the topological representation of PDCs (n=462 biologically independent samples). Each node represents a set of PDCs with similar AUC profiles. A PDC can appear in several nodes, and two nodes are connected by an edge if they have at least one PDC in common. The P values were calculated using the pearson correlation test between the fraction distribution of gastric or glioma cell lines and mean AUC values of BYL719 drug over the nodes and they were adjusted using BH method. (d) Violin plots measures the activity level of PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway on gastric and GBMs using TCGA RNASeq datasets (n=100 biologically independent samples for each group). We adopt the enrichment score derived from ssGSEA analysis as assessment. The P value is calculated from two-sided wilcox rank-sum test. Horizontal lines within the violin plot represent 0.25, 0.50, and 0.75 quantiles.