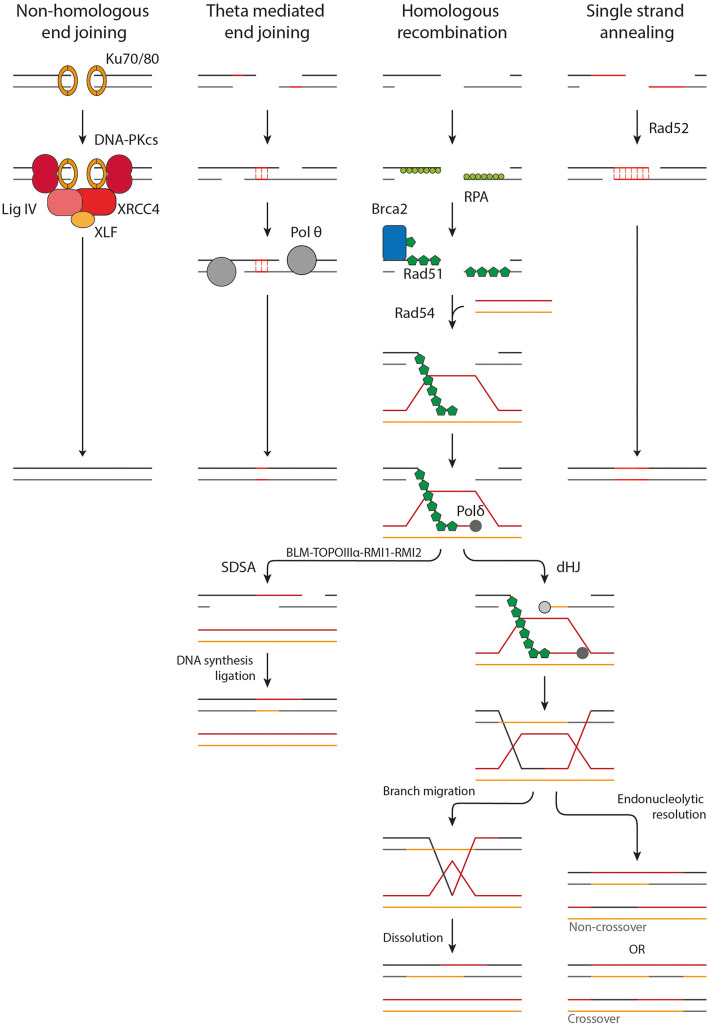
FIGURE 2.
Overview of the DSB repair pathways. NHEJ acts upon protected DSB ends. Ku70/80 binds to the DSB ends followed by the accumulation of DNA-PKcs, XRCC4, XLF, and LigIV. The DSB ends are processed and ligated. TMEJ acts on short-range resected ends. Microhomology of 2–20 bp is required to transiently align the DSB ends, after which the gaps are filled in by Pol θ. HR requires long-range resection and makes use of a homologous donor sequence for repair. After resection Rad51-loading onto the ssDNA is mediated by BRCA2. Homology search is facilitated by Rad54. Once a homologous donor strand has been found a D-loop is formed and DNA synthesis is started. In SDSA the D-loop is disrupted, followed by DNA synthesis and ligation to repair the DSB. A D-loop can also progress into the formation of a dHJ, which can be resolved by branch migration and dissolution or endonucleolytic resolution. Endonucleolytic resolution can result in a non-crossover or crossover product.