Figure 2.
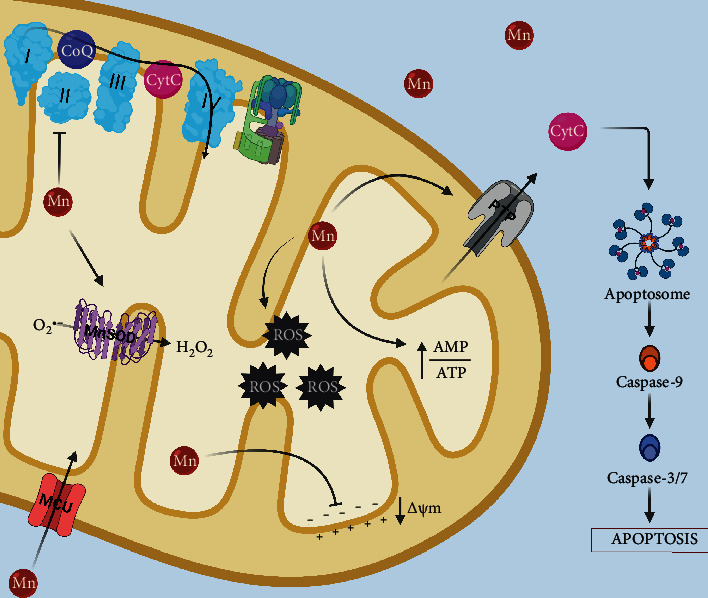
Effects of Mn exposure on mitochondrial function in glia. Once inside the cell, Mn is readily taken up by the mitochondria through the MCU, where exerts its toxic actions by producing free radicals and damaging the complex II of the electron transport chain, the excessive levels of Mn in the mitochondria can also affect Mn-SOD activity promoting hydrogen peroxide formation. Moreover, Mn depolarizes the mitochondrial membrane potential promoting the opening of the PTP, which allows the release of cytochrome C, triggering caspase-dependent apoptosis pathways.
