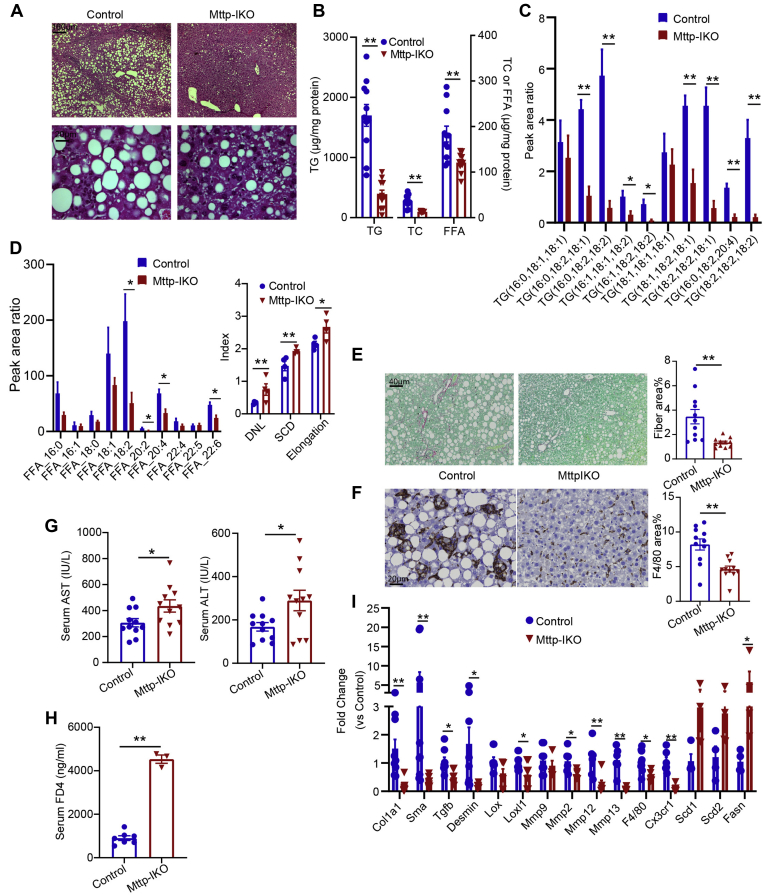
Fig. 1.
Conditional intestinal Mttp deletion prevents hepatic steatosis, fibrosis, and inflammation in male mice-fed MCD for 3 weeks. A: Representative images of H&E-stained liver tissue at 50× (upper panels) and 400× magnification. B: Biochemical quantitation of hepatic lipid content, including TG, FFAs, and total cholesterol (TC) (n = 11/genotype). C: Relative abundance of the most abundant TG species presented as peak area ratio (n = 4/group). D: Relative abundance of the most abundant FFA species presented as peak area ratio (left panel). Right panel shows indices of DNL, FA saturation (SCD), and elongation (n = 4/genotype) calculated from peak area of all FFA species. E: Representative images of Sirius red-stained liver tissue (200× magnification). Right panel shows quantitation of fibrotic area, expressed as percent of total tissue area (n = 11/genotype). F: Representative images of F4/80 staining (400×). Right panel shows quantitation of F4/80-stained area expressed as percent of total tissue area (n = 11/genotype). G: Serum AST (left) and ALT levels (n = 11/genotype). H: Serum FITC-dextran (FD4) levels 2 h after oral gavage (n = 3–7/genotype). I: mRNA expression of genes related to fibrosis, inflammation, and lipogenesis (n = 4–11/genotype). For all panels, data are presented as mean ± SEM, with ∗ indicating P < 0.05 and ∗∗ indicating P < 0.01. AST, aspartate aminotransferase.