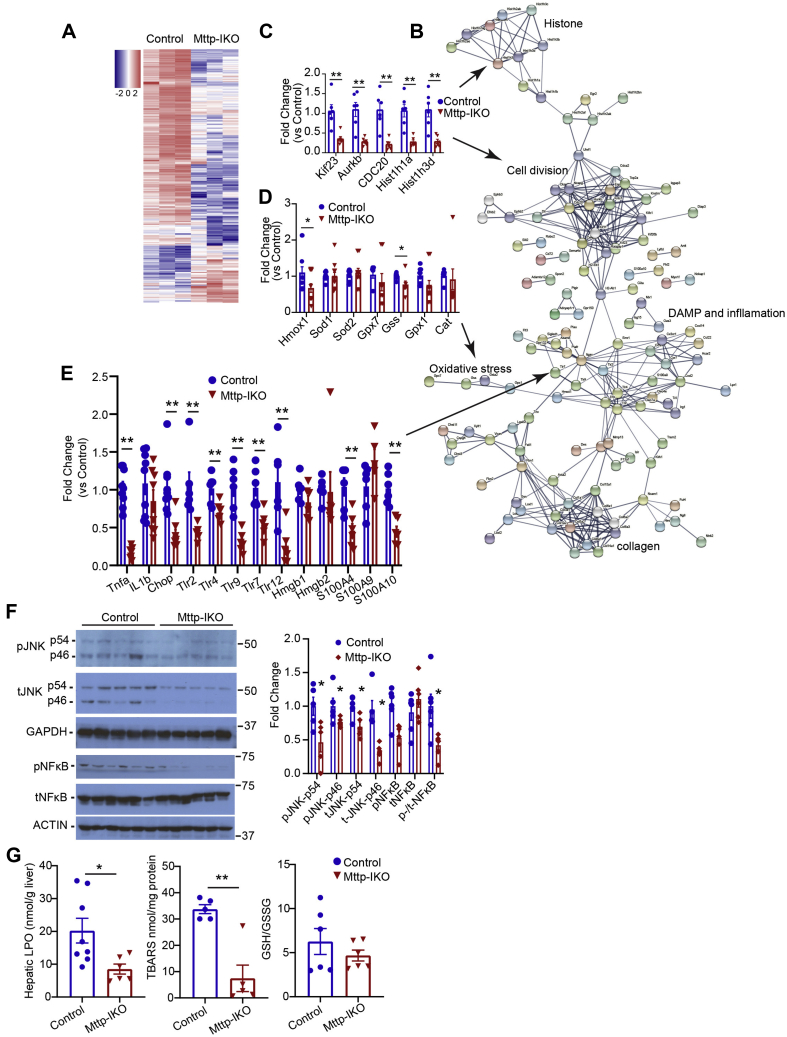
Fig. 2.
Intestinal Mttp deletion attenuates expression of liver damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and oxidative stress induced by MCD feeding in male mice. A: Heat map of 290 differentially expressed genes (log fold change [FC] ≥ ±2) in control and Mttp-IKO liver. B: STRING analysis of 205 differentially expressed genes with log (FC) ≤ −2 showing enriched pathways. C–E: Quantitative PCR validation of gene clusters involved in cell division (C), oxidative stress (D), and DAMP and inflammation (E) associated STRING pathways. F: Expression of total and phosphorylated JNK and NF-κB proteins in control and Mttp-IKO liver tissue. A representative Western blot (left) and quantitation of protein levels relative to controls after normalization to loading controls (GAPDH or ACTIN) are shown. G: Biochemical determination of hepatic lipid hydroperoxide (LPO, left panel) and TBARS (middle) levels. Right panel shows ratio of GSH to GSSG. For all bar graphs, data are presented as mean ± SEM, with n = 4–9/genotype. ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01.