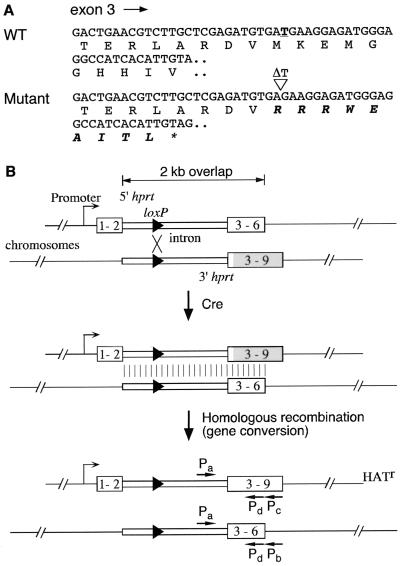
FIG. 2.
A frameshift mutation in the original 3′ hprt cassette used in chromosome engineering. (A) Partial exon 3 sequence of the wild-type (WT) and mutant 3′ hprt cassette with conceptual translation. The thymidine residue in the wild-type sequence that is deleted in the mutant is in boldface and underlined. The altered amino acid residues affected by the mutation is in italicized boldface. ∗, Stop codon. (B) A proposed mechanism by which HAT-resistant colonies were obtained by a combination of Cre-loxP site-specific recombination and homologous recombination, as shown for Cre recombination between two loxP sites in trans in the same orientation that leads to a deletion and a duplication. 1–2, 3–6, and 3–9 refer to Hprt exons. Pa, Pb, Pc, and Pd, primers for PCR and sequence analysis of exon 3 of the Hprt gene. The portion of the coding sequence affected by the mutation in exons 3–9 is shaded. The polyadenylation signal and neomycin and puromycin resistance genes are not shown for simplicity.