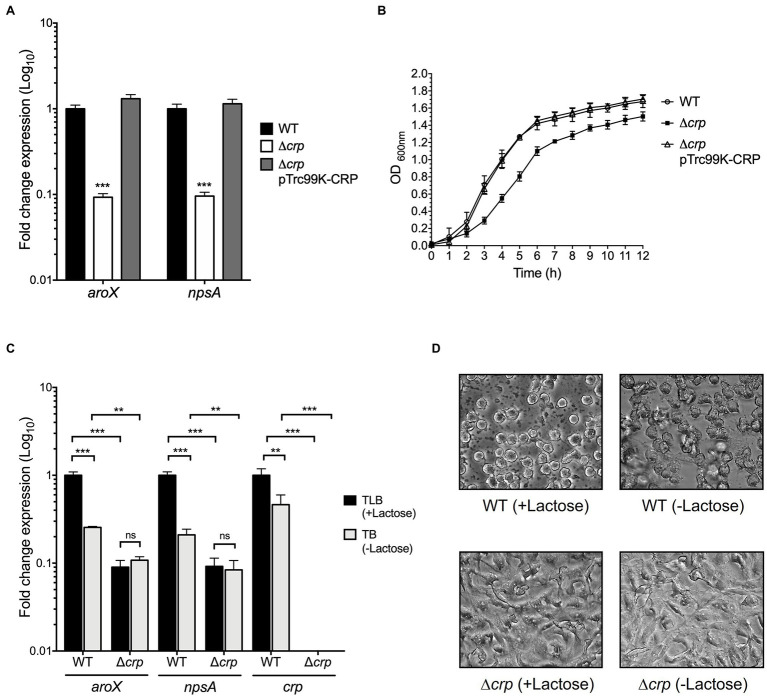
Figure 2.
Regulatory activity of CRP in expression of aroX and npsA genes. (A) Determination of transcriptional expression by RT-qPCR of aroX and npsA genes of wild-type K. oxytoca, Δcrp, and Δcrp pTrc99K-CRP in TLB medium at stationary phase (OD600nm=1.6) at 37°C. (B) Growth curves of wild-type K. oxytoca, Δcrp, and Δcrp pTrc99K-CRP, in TLB medium at 37°C. Bacterial cultures were grown for 12h. (C) Transcription of aroX, npsA, and crp genes at stationary phase (OD600nm=1.6) at 37°C determined by RT-qPCR in TLB (medium with lactose), and TB (medium without lactose) at 37°C for 12h. These graphs represent the mean of three independent experiments performed in triplicate with standard deviations. (D) HeLa cell culture inoculated with supernatants recovered from wild-type and Δcrp strains grown in TLB (medium with lactose) and TB (medium without lactose). Results represent the mean of three independent experiments performed in triplicate with standard deviations. Statistically significant with respect to wild-type strain (A) or with respect to bacteria grown in TLB medium (B): **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. All Values of p were calculated using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s comparison test.