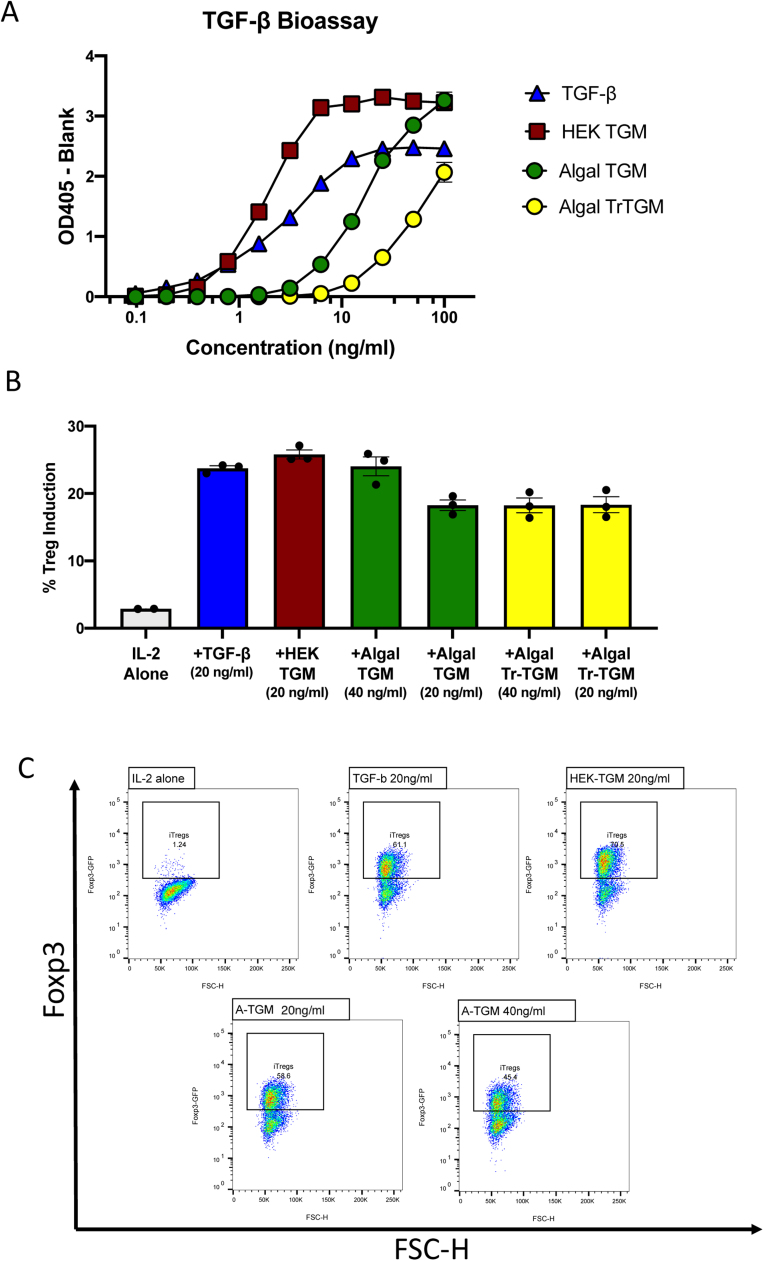
Fig. 2.
FLAG-purified algal TGM1 and its bioactivity on TGF-β-responsive cell assays. A. MFB-F11 TGF-β receptor binding assay. MFB-F11 cells encode a Smad-responsive reporter construct which induces secretion of alkaline phosphatase following ligation of the TGF-β receptors; alkaline phosphatase is detected by addition of p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate generating a color reaction. Cells were incubated with mammalian TGF-β, HEK293 expressed TGM1, οr algal secreted TGM1 / ΤrTGM1 at the indicated concentrations and separately for 24 h, before recovery of supernatants for enzyme assay with p-nitrophenyl phosphate substrate. Data represent one of two similar experiments. B. Naïve T cells from transgenic mice encoding a Foxp3-GFP fusion protein (Fontenot et al., 2005) respond to TGF-β receptor ligation by expression of GFP that is detected by flow cytometry. Induction of primary mouse splenic CD4+ T cells to Foxp3-GFP expression. Data represent one of two similar experiments. C. Representative flow cytometry plots of Foxp3-GFP reporter T cells treated with TGF-β or TGM1 from mammalian (HEK) or algal (A-TGM) expression systems, together with IL-2. Control cultures received IL-2 alone. Forward Scatter (FSC-H) and Foxp3 expression and are plotted on the X and Y axes, with the same gate for positive cells for all samples.