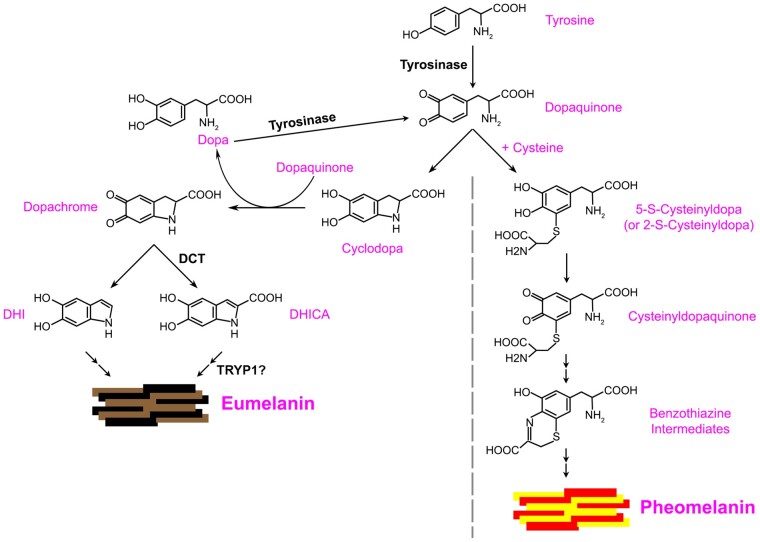
Fig. 1.
Model of eumelanin synthesis. TYR catalyzes the oxidation of tyrosine to generate dopaquinone. In the presence of cysteine, dopaquinone is spontaneously converted to pheomelanin via 5-S-cysteinyldopa or 2-S-cysteinyldopa, cysteinyldopaquinone, and benzothiazine intermediates. In the absence of cysteine, dopaquinone can spontaneously cyclize to cyclodopa, and subsequent spontaneous redox exchange of cyclodopa with dopaquinone gives rise to dopachrome and L-dopa (Cooksey et al. 1997; Ramsden and Riley 2014); L-dopa can then be oxidized by TYR to form more dopaquinone. Dopachrome can spontaneously reorganize to form DHI or can undergo tautomerization by DCT to form DHICA. Both DHI and DHICA undergo oxidation and polymerization to form eumelanins. TYRP1 might support DHICA polymerization either directly or indirectly, or alternatively serve either as a chaperone for TYR or as an antioxidant sink. Adapted from Ito and Wakamatsu (2008).