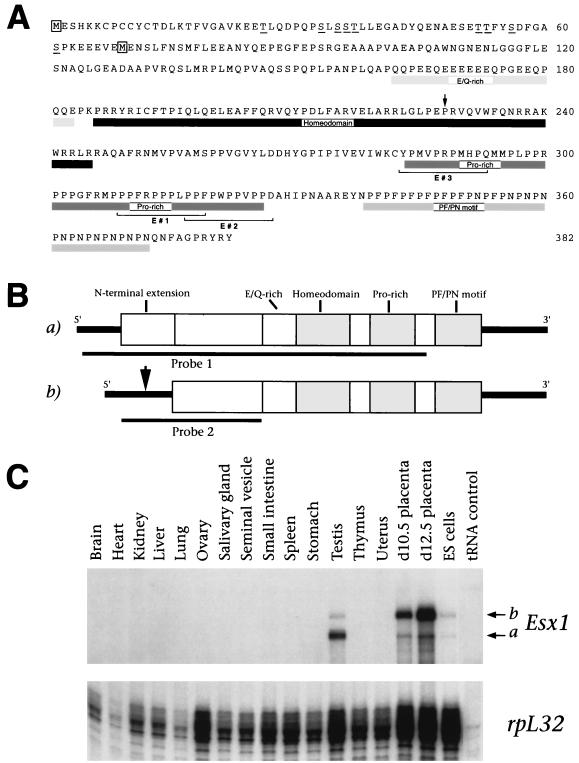
FIG. 1.
Differential expression of alternative Esx1 transcripts in the placenta and testes. (A) Amino acid sequence encoded by the longest Esx1 transcript (transcript A) (5). The putative initiator methionines for the products of transcripts A and B are boxed (transcript B) (26). Protein domains are indicated by boxes, the proline-rich peptides (E#1, E#2, and E#3) are bracketed, potential phosphorylation sites in the N-terminal extension are underlined, and the proline at position 43 of the homeodomain is indicated by an arrow. (B) Schematic diagram of the protein products of transcripts A and B. The protein regions depicted are the N-terminal extension, the glutamic acid- and glutamine-rich region (E/Q-rich), the homeodomain, the proline-rich region (Pro-rich), and the PF/PN motif. The arrow indicates the position in transcript B where its nucleotide sequence diverges at the 5′ end from transcript A. Probes for in situ hybridization (probe 1) and RNase protection assays (probe 2) are indicated. (C) RNase protection analysis of Esx1 transcripts. Each hybridization mixture contained 15 μg of total RNA (or 50 μg of yeast tRNA) and antisense riboprobes for Esx1 (probe 2) and ribosomal protein L32 (rpL32) as an internal standard (43). The positions of protected fragments corresponding to transcripts A and B are indicated.