FIGURE 8.
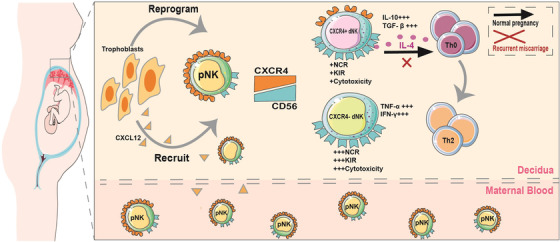
Schematic diagram illustrating the origin, phenotype and function of CXCR4+CD56bright dNKs in maternal–foetal immune tolerance during early pregnancy. Trophoblasts attract peripheral CXCR4+ NK through secreting CXCL12. Trophoblasts further upregulate CD56 and downregulate CXCR4 expression of CXCR4+ pNK to adopt a dNK‐similar phenotype. CXCR4+CD56bright dNK are the main source of IL‐4 at maternal–foetal interface, which induce CD4+CD45RA+ naïve T cells to preferentially differentiate to Th2‐type cells, involving in the maintenance of normal pregnancy. In miscarriage, the number and IL‐4‐prodution of CXCR4+CD56bright NK cells in the decidua are compromised, which fail to promote Th2 bias at maternal–foetal interface
