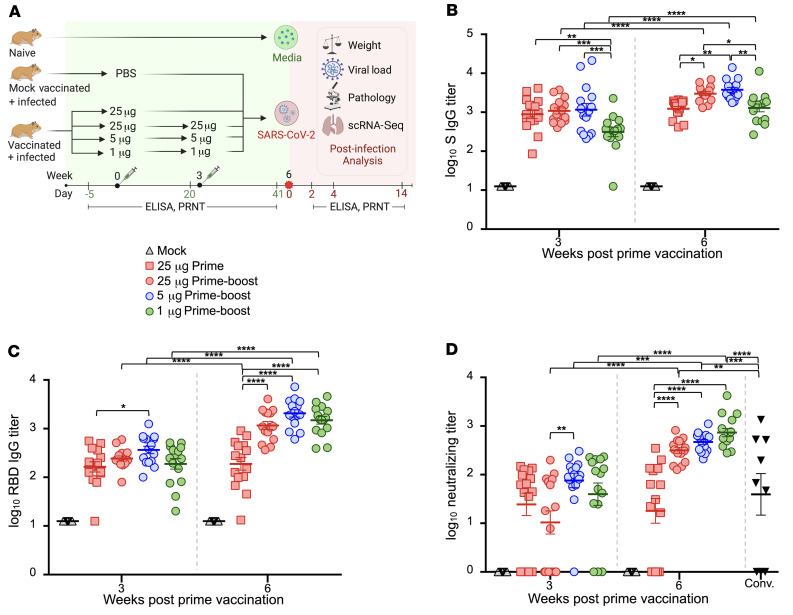
Figure 1. Serum antibody responses in vaccinated hamsters.
(A) Study design. Hamsters were prime-vaccinated via the i.m. route at week 0 and boosted at week 3, with 25 μg (n = 15), 5 μg (n = 15), and 1 μg (n = 15) of mRNA-1273. A group of hamsters (n = 15) received a prime dose only of 25 μg mRNA-1273, and a mock group received PBS (n = 15) at week 0. At week 6, animals were intranasally challenged with 105 PFU of SARS-CoV-2. On days 2, 4, and 14 after infection, hamsters (n = 5 per group) were euthanized for tissue collection. PRNT, plaque reduction neutralization test (B–D) Total serum SARS-CoV-2 S–specific (B) and RBD-specific (C) IgG titers in serum and neutralizing titers (D) in hamster groups prior to SARS-CoV-2 infection measured by ELISA and plaque reduction assays, respectively. Neutralizing titers were compared with a panel of human convalescent serum samples (Conv.). Bars denote group means ± SE. Significance was measured by ANOVA with Tukey’s or Šidák’s correction for multiple comparisons between vaccine groups or between time points, respectively (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001).