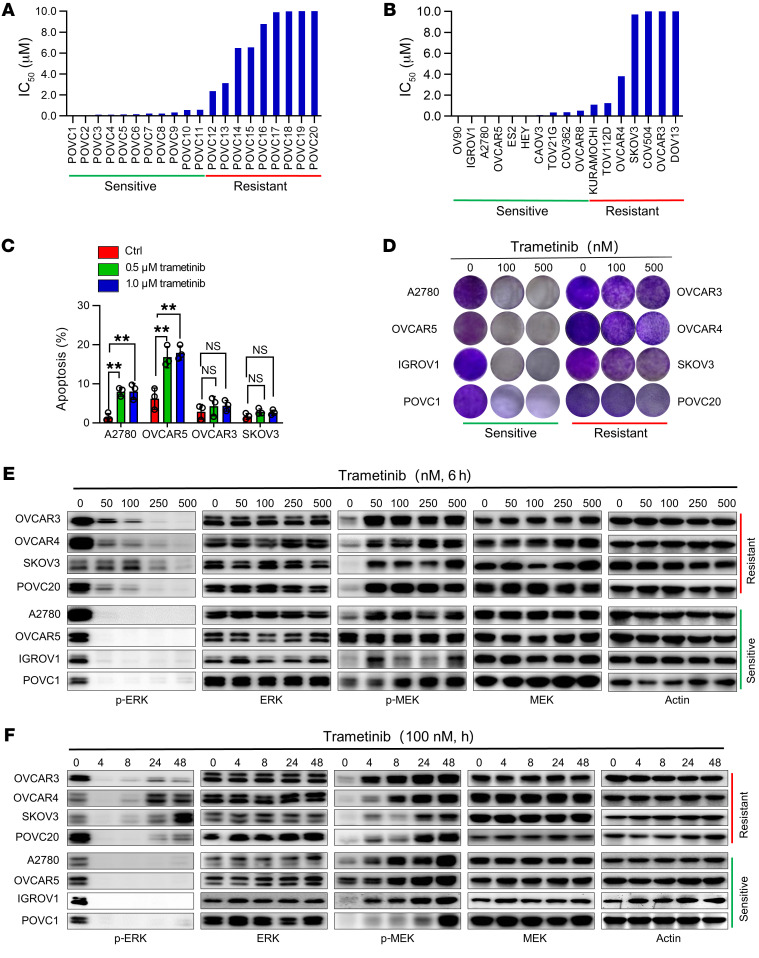
Figure 1. In vitro effect of MEK inhibitor in OV models.
(A and B) Growth-inhibitory effect of trametinib on 20 patient-derived primary cells (A) and 17 commercial OV cell lines (B). Cells were treated with vehicle or different dosages of trametinib in a 4-day cell viability assay. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values for trametinib are represented on the y axis. Data represent the mean of 3 biological replicates. The cutoff value of IC50 for sensitivity is 1.0 μM. (C) Quantification of the apoptotic cells in 2 sensitive cell lines (A2780 and OVCAR5) and 2 resistant cell lines (OVCAR3 and SKOV3) treated with vehicle or trametinib (500 nM or 1 μM) for 72 hours, analyzed by flow cytometry. Results are represented as mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01 by 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (D) Colony formation assay in 4 sensitive (A2780, OVCAR5, IGROV1, and POVC1) and 4 resistant (OVCAR3, OVCAR4, SKOV3 and POVC20) OV commercial cell lines and patient-derived cells. Cells were treated with vehicle or trametinib (100 or 500 nM) for 10–12 days. Images are representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) Immunoblot analysis of MEK/ERK signaling in sensitive and resistant cells treated with increasing concentrations of trametinib for 6 hours. (F) Immunoblot analysis of MEK/ERK signaling in sensitive and resistant cells treated with 100 nM trametinib at indicated time points.