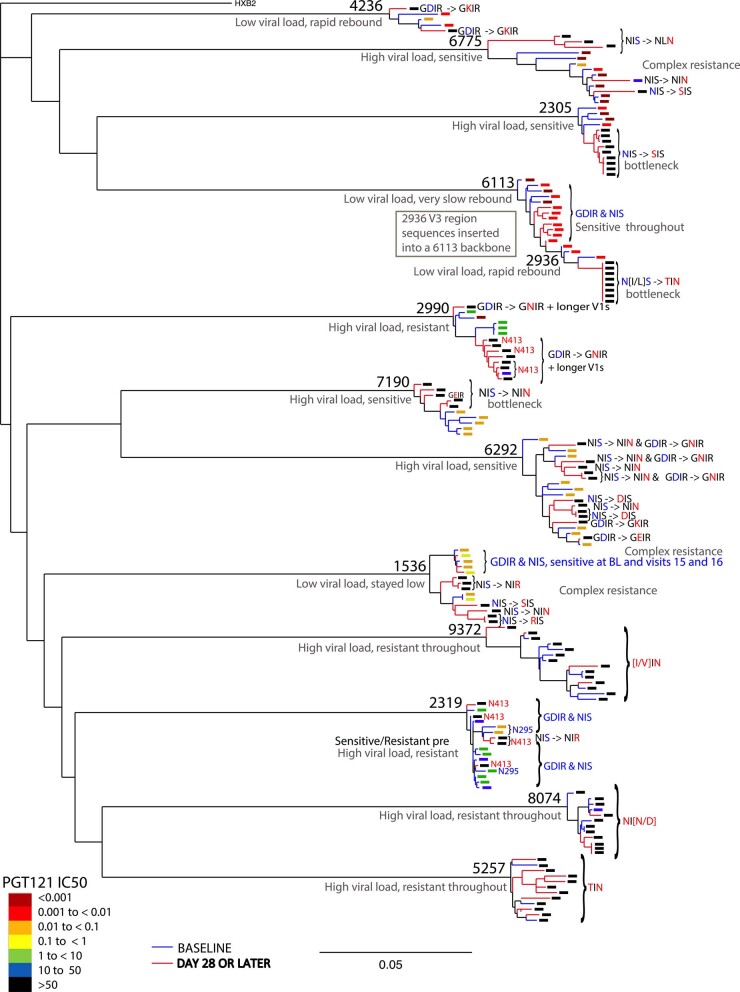
Extended Data Fig. 5. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of HIV-1 Env sequences isolated from participants pre- and post-PGT121 treatment.
The branch colors indicate sequences sampled at baseline (blue) versus post-PGT121 treatment (red). The colored box at every leaf indicates PGT121 sensitivity as an IC50 score in a TZM.bl assay; black is undetectable, blue and green are relatively resistant, and yellow-through-red increasingly sensitive. The likely amino acids that confer PGT121 resistance mutation are indicated to the right of the branches. If a four-letter motif is indicated, it represents positions 324–327 (HXB2 numbering), a conserved part PGT121 epitope; GDIR is the common consensus form and is associated with antibody sensitivity. If a three-letter motif is indicated, it refers to positions 332–334; most commonly this is a glycosylation site (NIS), and an N-linked glycan is generally critical for V3 bNAb sensitivity. Blue letters indicate PGT121 sensitive signature amino acids, red indicate resistant. The glycosylation motif can be lost by either the loss of the Asn (N) at N332, or the loss of a Thr (T) or Ser (S) at S334. D325 is the most variable position in the highly conserved GDIR motif. D325N does not always confer resistances (for example participant 6775), but is generally associated with resistance (for example participants 6292 and 2990).