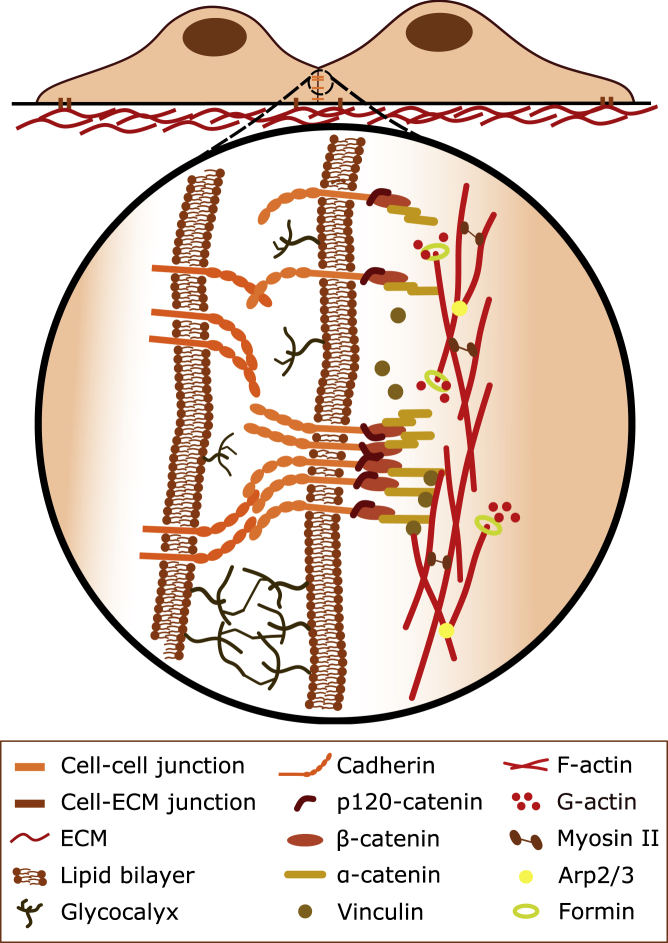
Figure 1.
Cells can undergo adhesions with other cells and the extracellular matrix (ECM) via junctions. Cadherins mediate specific cell-cell adhesions via trans interactions in the extracellular space, where glycocalices act as a repulsive barrier. Cadherins indirectly bind to the underlying actomyosin cortex via β- and ɑ-catenins. Mechanosensitive cadherin adhesion complexes can change their binding strength to the actin cortex by cis clustering and by recruiting adaptor proteins such as vinculin. These complexes can also lead to local changes in actomyosin contractility by regulating the architecture of the cortex.