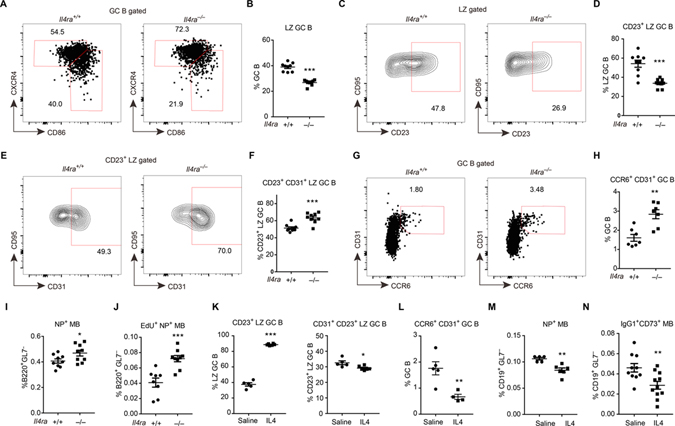
Figure 4. IL4Ra signaling restrains memory B cell development at the CD23+ LZ stage.
(A-I) Immunized Il4ra+/+ and Il4ra−/− mice were analyzed on day 13. (A, B) Representative FACS profiles (A) and frequencies of CXCR4lo CD86hi LZ cells (B) in GC B cells. (C, D) Representative FACS profiles (C) and frequencies of CD23+ cells (D) in LZ GC B cells. (E, F) Representative FACS profiles (E) and frequencies of CD31+ cells (F) in CD23+ LZ GC B cells. (G, H) Representative FACS profiles (G) and frequencies of CD31+ CCR6+ cells (H) in GC B cells. (I) Frequencies NP+ memory B cells in B220+ GL7− non-GC B cells. Data are pooled from two experiments. (J) Immunized Il4ra+/+ and Il4ra−/− mice were treated with EdU on day 11 post immunization and were analyzed on day 14. Frequencies of NP+ EdU+ memory B cells in B220+ GL7− non-GC B cells. Data are pooled from two experiments. (K-N) Immunized mice received IL4-αIL4 complex or saline on day 11, 12, 13 post immunization and were analyzed on day 14. (K, L) Frequencies of CD23+ cells in LZ GC B cells (K left), CD31+ cells in CD23+ LZ GC B cells (K right), and CD31+CCR6+ cells in GC B cells (L). (M, N) Frequencies of NP+ memory B cells (M) and IgG1+ CD73+ memory B cells (N) in CD19+ GL7− non-GC B cells. Each symbol represents one mouse. (K-M) One of three experiments with similar result is shown. (N) Data are pooled from three experiments. See also Figure S3.